Anaerobic Faecalicatena spp. degrade sulfoquinovose via a bifurcated 6-deoxy-6-sulfofructose transketolase/transaldolase pathway to both C2- and C3-sulfonate intermediates
- PMID: 39712897
- PMCID: PMC11659671
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1491101
Anaerobic Faecalicatena spp. degrade sulfoquinovose via a bifurcated 6-deoxy-6-sulfofructose transketolase/transaldolase pathway to both C2- and C3-sulfonate intermediates
Abstract
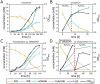
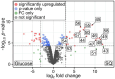
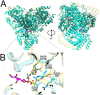
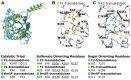
Plant-produced sulfoquinovose (SQ, 6-deoxy-6-sulfoglucose) is one of the most abundant sulfur-containing compounds in nature and its bacterial degradation plays an important role in the biogeochemical sulfur and carbon cycles and in all habitats where SQ is produced and degraded, particularly in gut microbiomes. Here, we report the enrichment and characterization of a strictly anaerobic SQ-degrading bacterial consortium that produces the C2-sulfonate isethionate (ISE) as the major product but also the C3-sulfonate 2,3-dihydroxypropanesulfonate (DHPS), with concomitant production of acetate and hydrogen (H2). In the second step, the ISE was degraded completely to hydrogen sulfide (H2S) when an additional electron donor (external H2) was supplied to the consortium. Through growth experiments, analytical chemistry, genomics, proteomics, and transcriptomics, we found evidence for a combination of the 6-deoxy-6-sulfofructose (SF) transketolase (sulfo-TK) and SF transaldolase (sulfo-TAL) pathways in a SQ-degrading Faecalicatena-phylotype (family Lachnospiraceae) of the consortium, and for the ISE-desulfonating glycyl-radical enzyme pathway, as described for Bilophila wadsworthia, in an Anaerospora-phylotype (Sporomusaceae). Furthermore, using total proteomics, a new gene cluster for a bifurcated SQ pathway was also detected in Faecalicatena sp. DSM22707, which grew with SQ in pure culture, producing mainly ISE, but also 3-sulfolacate (SL) 3-sulfolacaldehyde (SLA), acetate, butyrate, succinate, and formate, but not H2. We then reproduced the growth of the consortium with SQ in a defined co-culture model consisting of Faecalicatena sp. DSM22707 and Bilophila wadsworthia 3.1.6. Our findings provide the first description of an additional sulfoglycolytic, bifurcated SQ pathway. Furthermore, we expand on the knowledge of sulfidogenic SQ degradation by strictly anaerobic co-cultures, comprising SQ-fermenting bacteria and cross-feeding of the sulfonate intermediate to H2S-producing organisms, a process in gut microbiomes that is relevant for human health and disease.
Keywords: 3-sulfolactaldehyde; 6-deoxy-6-sulfofructose transaldolase; anaerobic microbial metabolism; carbon and sulfur cycle; isethionate; transketolase.
Copyright © 2024 Borusak, Denger, Dorendorf, Fournier, Lerner, Mayans, Spiteller and Schleheck.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
A Variant of the Sulfoglycolytic Transketolase Pathway for the Degradation of Sulfoquinovose into Sulfoacetate.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Jul 26;89(7):e0061723. doi: 10.1128/aem.00617-23. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37404184 Free PMC article.
-
Anaerobic Degradation of the Plant Sugar Sulfoquinovose Concomitant With H2S Production: Escherichia coli K-12 and Desulfovibrio sp. Strain DF1 as Co-culture Model.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 27;9:2792. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02792. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30546350 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental and Intestinal Phylum Firmicutes Bacteria Metabolize the Plant Sugar Sulfoquinovose via a 6-Deoxy-6-sulfofructose Transaldolase Pathway.iScience. 2020 Aug 28;23(9):101510. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101510. eCollection 2020 Sep 25. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32919372 Free PMC article.
-
New mechanisms for bacterial degradation of sulfoquinovose.Biosci Rep. 2022 Oct 28;42(10):BSR20220314. doi: 10.1042/BSR20220314. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36196895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulfoglycolysis: catabolic pathways for metabolism of sulfoquinovose.Chem Soc Rev. 2021 Dec 13;50(24):13628-13645. doi: 10.1039/d1cs00846c. Chem Soc Rev. 2021. PMID: 34816844 Review.
Cited by
-
Sulfoquinovose is exclusively metabolized by the gut microbiota and degraded differently in mice and humans.Microbiome. 2025 Aug 7;13(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s40168-025-02175-x. Microbiome. 2025. PMID: 40775374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrew S. (2015) FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data 2015 (updated June). Available at: https://qubeshub.org/resources/fastqc.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

