Prognostic Impact of CCA Components in Combined Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 39712948
- PMCID: PMC11663380
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S491243
Prognostic Impact of CCA Components in Combined Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the differences of combined hepatocellular carcinoma-cholangiocarcinoma (cHCC-CCA) patients with a cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) component ≥ 30% or < 30% versus intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) patients in recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) prognoses.
Methods: Patients with cHCC-CCA and iCCA after surgery were recruited. All cHCC-CCA patients were divided into two subgroups (CCA components ≥ 30% and < 30%). Then, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox regression analysis were used to investigate and compare the differences of cHCC-CCAs with a CCA component ≥ 30% or < 30% versus iCCAs in RFS and OS prognoses, respectively. The differences of MRI features between cHCC-CCAs with a CCA component ≥ 30% and < 30% were also compared.
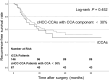
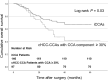
Results: One hundred sixty-four cHCC-CCAs and 146 iCCAs were enrolled. Compared with iCCAs, cHCC-CCAs with a CCA component < 30% had better OS prognosis (HR: 2.888, p = 0.045). However, Cox regression analysis revealed that cHCC-CCAs with a CCA component ≥ 30% had poorer RFS (HR: 0.503, p < 0.001) and OS (HR: 0.58, p = 0.033) prognoses than iCCAs. In addition, rim APHE (OR = 0.286, p < 0.001), targetoid diffusion restriction (OR = 0.316, p = 0.019), corona enhancement (OR = 0.481, p = 0.033), delayed enhancement (OR = 0.251, p = 0.001), and LR-M (OR = 1.586, p < 0.001) were significant factors associated with cHCC-CCAs with a CCA component ≥ 30%. Multivariable regression analyses showed that only LR-M (OR = 1.522, p = 0.042) was a significantly independent predictor for cHCC-CCAs with a CCA component ≥ 30%.
Conclusion: cHCC-CCAs with a CCA component ≥ 30% had worse prognoses than iCCAs. Therefore, we suggest that the postoperative treatment of cHCC-CCAs with a CCA component ≥ 30% can be based on the treatment strategy for iCCAs.
Keywords: liver neoplasms; magnetic resonance imaging; prognosis.
© 2024 Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no conflicts of interest in this work. All participants are informed about the purpose of the study, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Figures


References
-
- Yen CC, Yen CJ, Shan YS, et al. Comparing the clinicopathological characteristics of combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma with those of other primary liver cancers by use of the updated World Health Organization classification. Histopathology. 2021;79:556–572. doi: 10.1111/his.14384 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

