Blood biomarkers to detect functional impairment in adult patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot
- PMID: 39712984
- PMCID: PMC11657782
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcchd.2023.100483
Blood biomarkers to detect functional impairment in adult patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot
Abstract
Background: The relationship between plasma brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and soluble suppression of tumorigenicity-2 (sST2) with structural adaptions and exercise capacity remains incompletely described in patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot (rTOF).
Methods: Peripheral venous blood samples were drawn for 99 patients with repaired TOF, 59 patients with severe pulmonary regurgitation (PR) and 40 patients with no or mild PR. NT-proBNP was measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, IN). Soluble ST2 levels were assessed on Aspect-plus ST2 quantitative rapid test.
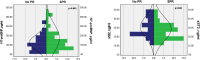
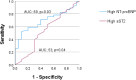
Results: The mean value of NT-proBNP was 160 ± 137 pg/ml, and sST2 was 29 ± 13, ng/ml in the entire population. 58 % had an elevated NT-proBNP, while sST2 was abnormal in 40 %. Mean NT-proBNP was significantly higher in patients with severe PR (169 ± 150 vs145 ± 118, pg/ml, p < 0.001), while similar sST2 levels were observed in both groups (29 ± 14 vs30 ± 12, ng/ml, p > 0.05). NT-proBNP and sST2 levels were higher in patients with transannular patch when compared to other RVOT intervention (174 ± 145 vs 107 ± 100, pg/ml, p < 0.001); (31 ± 13 vs 29 ± 15, ng/ml, p < 0.05). Both biomarkers were significantly associated with exercise capacity, but NT-proBNP (r = -0.60, p < 0.001) was stronger. The optimal cut-off of 90 pg/ml for NT-proBNP had a sensitivity of 74 % and specificity of 63 % for detection of impaired exercise capacity.
Conclusions: Serum levels of sST2 and NT-proBNP are elevated in patients with repaired TOF, with higher values observed in those with severe PR, but also in patients undergoing transannular patch repair. Incorporating both markers in these patients increased the ability to detect impairment in exercise capacity.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Ponikowski P., Voors A., Anker S., Bueno H., Cleland J., Coats A., et al. The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2129–2200. - PubMed
-
- Yoo B.S., Kim W.J., Jung H.S., Kim J.Y., Lee S.W., Hwang S.O., et al. The clinical experiences of B-type natriuretic peptide blood concentrations for diagnosis in congestive heart failure: the single hospital experience based on the large clinical database. Korean Circulation Journal. 2004;34(7):684–692.
-
- Daniels L.B., Bayes-Genis AJFc. Using ST2 in cardiovascular patients: a review. Future Cardiol. 2014;10(4):525–539. - PubMed
-
- Gaggin H.K., Szymonifka J., Bhardwaj A., Belcher A., De Berardinis B., Motiwala S., et al. Head-to-head comparison of serial soluble ST2, growth differentiation factor-15, and highly-sensitive troponin T measurements in patients with chronic heart failure. JACC (J Am Coll Cardiol): Heart Fail. 2014;2(1):65–72. - PubMed
-
- Norozi K., Buchhorn R., Kaiser C., Hess G., Grunewald R.W., Binder L., et al. Plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide as a marker of right ventricular dysfunction in patients with tetralogy of Fallot after surgical repair. Chest. 2005;128(4):2563–2570. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

