Facing stress and inflammation: From the cell to the planet
- PMID: 39713080
- PMCID: PMC11551703
- DOI: 10.5493/wjem.v14.i4.96422
Facing stress and inflammation: From the cell to the planet
Abstract
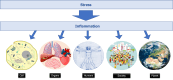
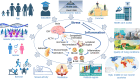
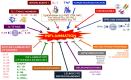
As identified in 1936 by Hans Selye, stress is shaping diseases through the induction of inflammation. But inflammation display some yin yang properties. On one hand inflammation is merging with the innate immune response aimed to fight infectious or sterile insults, on the other hand inflammation favors chronic physical or psychological disorders. Nature has equipped the cells, the organs, and the individuals with mediators and mechanisms that allow them to deal with stress, and even a good stress (eustress) has been associated with homeostasis. Likewise, societies and the planet are exposed to stressful settings, but wars and global warming suggest that the regulatory mechanisms are poorly efficient. In this review we list some inducers of the physiological stress, psychologic stress, societal stress, and planetary stress, and mention some of the great number of parameters which affect and modulate the response to stress and render it different from an individual to another, from the cellular level to the societal one. The cell, the organ, the individual, the society, and the planet share many stressors of which the consequences are extremely interconnected ending in the domino effect and the butterfly effect.
Keywords: Climate change; Cytokines; Genetic diversity; Global health; Immunity; Microplastics; Resilience; Yin yang.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Is cancer a severe delayed hypersensitivity reaction and histamine a blueprint?Clin Transl Med. 2016 Dec;5(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40169-016-0108-3. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Clin Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27558401 Free PMC article.
-
"Stress" is 80 Years Old: From Hans Selye Original Paper in 1936 to Recent Advances in GI Ulceration.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(27):4029-4041. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170622110046. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28641541 Review.
-
A concept for international societally relevant microbiology education and microbiology knowledge promulgation in society.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 May;17(5):e14456. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14456. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38801001 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of T Cell Immunity in Atopic Dermatitis by Microbes: The Yin and Yang of Cutaneous Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2015 Jul 13;6:353. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00353. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26217343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deceptology in cancer and vaccine sciences: Seeds of immune destruction-mini electric shocks in mitochondria: Neuroplasticity-electrobiology of response profiles and increased induced diseases in four generations - A hypothesis.Clin Transl Med. 2020 Dec;10(8):e215. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.215. Clin Transl Med. 2020. Retraction in: Clin Transl Med. 2021 May;11(5):e389. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.389. PMID: 33377661 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
References
-
- Ghezzi P. Societal factors in network medicine and causation. Front Sci. 2024;2
-
- Androulakis IP. From cells to society: untangling the web of stress, inflammation, and social determinants of health. Front Sci. 2024;2
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

