Who is Focusing on Women's Health: A Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research Trends on Overweight in Female Patients with Gynecologic or Breast Cancer
- PMID: 39713093
- PMCID: PMC11662632
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S496718
Who is Focusing on Women's Health: A Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research Trends on Overweight in Female Patients with Gynecologic or Breast Cancer
Abstract
Objective: Obesity has become a significant public health concern, strongly linked to various diseases, particularly gynecologic and breast cancers. This bibliometric review aims to analyze global research trends on overweight women, particularly those with gynecologic and breast cancers, to identify research hotspots, key contributors, and emerging areas of study.
Methods: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis was conducted using the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database, covering the period from January 2013 to September 2024. Articles were screened and analyzed using tools such as VOSviewer and Biblioshiny platform, with metrics including publication volume, citation analysis, and co-authorship networks. Key areas of focus were global research trends, leading countries, institutions, authors, journals, and keyword analysis.
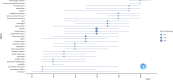
Results: A total of 1452 publications were analyzed. Research activity on the association between obesity and gynecologic/breast cancer has steadily increased, with the United States leading in publications and citations, followed by China and Italy. Core journals included Breast Cancer Research and Treatment and Gynecologic Oncology. Key research areas identified through keyword analysis include the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and cancer risk, survival rates in cancer patients, physical activity, and the role of adipose tissue inflammation in tumor progression. Emerging topics include extracellular vesicles and cancer-associated fibroblasts.
Conclusion: Global research on the relationship between obesity and female-specific cancers has shown significant growth. The findings highlight BMI, survival, and physical activity as central themes. Future research should explore the molecular mechanisms linking obesity to cancer and evaluate weight loss interventions for cancer prevention and treatment.
Keywords: bibliometrics; breast cancer; gynecologic cancer; obesity; women health.
© 2024 Gu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
A bibliometric and visual analysis of cancer-associated fibroblasts.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 19;14:1323115. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1323115. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38173726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometric analysis of worldwide research trends on breast cancer about inflammation.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 19;13:1166690. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1166690. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37152044 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric and visualized analysis of ocular drug delivery from 2001 to 2020.J Control Release. 2022 May;345:625-645. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.03.031. Epub 2022 Mar 20. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35321827 Review.
-
Exploring research trends and hotspots on oxidative stress and bronchopulmonary dysplasia: Insights from bibliometric and visualized study.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2024 Dec;59(12):3610-3623. doi: 10.1002/ppul.27268. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2024. PMID: 39264135
References
-
- Vivoni S, Garratón F, Carro M, González-Sepúlveda L, Romaguera J, Umpierre S. Knowledge of obesity’s health related outcomes among Hispanic women living in Puerto Rico. P R Health Sci J. 2023;42(4):291–297. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

