Cytotoxic Effects of Pulp Capping Agents on Mesenchymal Stem Cells Isolated from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth
- PMID: 39713113
- PMCID: PMC11662175
- DOI: 10.30476/dentjods.2023.99173.2131
Cytotoxic Effects of Pulp Capping Agents on Mesenchymal Stem Cells Isolated from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth
Abstract
Statement of the problem: Success of pulpotomy of primary teeth depends on biological and cytotoxic effects of pulp capping agents. Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), Biodentine, calcium enriched mixture (CEM) cement, and ferric sulfate (FS) are among the commonly used pulp capping agents (PCAs) for pulpotomy, and their successful application has been previously evaluated.
Purpose: This study aimed to compare the cytotoxicity of PCAs against mesenchymal stem cells isolated from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHEDs).
Materials and method: In this in vitro study, SHEDs were exposed to MTA, Biodentine, CEM cement, and FS for 24 and 72 hours. The methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium (MTT) assay was performed for five different concentrations of PCAs after 24 and 72 hours of exposure. Data were analyzed by ANOVA.
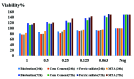
Results: Generally, the biocompatibility increased by reduction in concentration. All tested concentrations showed higher biocompatibility at 72 hours compared with 24 hours (p< 0.0001). Comparison of cytotoxicity of different biomaterials revealed no significant difference at any time point (p> 0.05).
Conclusion: In general, the cytotoxicity of MTA, Biodentine, CEM cement, and FS was comparable, with no significant difference. Cytotoxicity decreased over time and by a reduction in concentration of biomaterials. MTA and Biodentine showed maximum biocompatibility followed by FS, and CEM cement.
Keywords: Deciduous teeth; Dental pulp capping; Stem Cells; Tooth.
Copyright: © Journal of Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nayak UA, Wadhwa S, Kashyap N, Prajapati D, Mahuli AV, Sharma R. Knowledge and practice of and attitudes toward, pulp therapy in deciduous teeth among pediatric dentists in India. J Investig Clin Dent. 2018; 9: 1. - PubMed
-
- Collado-González M, García-Bernal D, Oñate-Sánchez RE, Ortolani-Seltenerich PS, Álvarez-Muro T, Lozano A, et al. Cytotoxicity and bioactivity of various pulpotomy materials on stem cells from human exfoliated primary teeth. Int Endod J. 2017; 50 Suppl 2: e19–e30. - PubMed
-
- Laurent P, Camps J, About I. Biodentine (TM) induces TGF-β1 release from human pulp cells and early dental pulp mineralization. Int Endod J. 2012; 45: 439–448. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
