Development and validation of a two-dimensional pseudorandom balance perturbation test
- PMID: 39713174
- PMCID: PMC11659295
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1471132
Development and validation of a two-dimensional pseudorandom balance perturbation test
Abstract
Introduction: Pseudorandom balance perturbations use unpredictable disturbances of the support surface to quantify reactive postural control. The ability to quantify postural responses to a continuous multidirectional perturbation in two orthogonal dimensions of sway (e.g., AP and ML) has yet to be investigated.
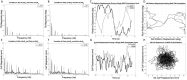
Methods: We developed a balance perturbation paradigm that used two spectrally independent sum of sinusoids signals (SoS1, SoS2), one for each orthogonal dimension of tilt (roll and pitch), to deliver a two-dimensional (2D) balance perturbation. In a group of 10 healthy adults we measured postural sway during 2D perturbations, as well as for each of the two individual 1D perturbation components.
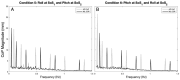
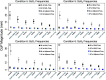
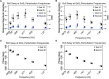
Results: We found that during 2D perturbations, spectral peaks in the sway response were larger at the perturbed frequencies when compared to (1) the adjacent non-perturbed frequencies and (2) the frequencies contained within the orthogonal, spectrally independent perturbation signal. We also found that for each of the two spectra (SoS1, SoS2), the magnitude and timing of the sway response relative to the platform disturbance was similar when measured during 1D and 2D conditions.
Discussion: These data support that our novel 2D SoS perturbation test was able to evoke ML and AP postural responses that were (1) specific to the roll and pitch perturbations, respectively, and (2) similar to the responses provoked by individual 1D perturbations.
Keywords: balance; multidimensional; perturbation; postural control; vestibular.
Copyright © 2024 Wagner, Chirumbole, Caccese, Chaudhari and Merfeld.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of Balance Training on Balance Performance in Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Sports Med. 2015 Dec;45(12):1721-38. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0375-y. Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 26325622 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical symptoms, signs and tests for identification of impending and current water-loss dehydration in older people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 30;2015(4):CD009647. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009647.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25924806 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
Pharmacological interventions for the prevention of bleeding in people undergoing elective hip or knee surgery: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jan 16;1(1):CD013295. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013295.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38226724 Free PMC article.
-
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for fibromyalgia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 9;10(10):CD012172. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012172.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28990665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campbell K. R., King L. A., Parrington L., Fino P. C., Antonellis P., Peterka R. J. (2022). Central sensorimotor integration assessment reveals deficits in standing balance control in people with chronic mild traumatic brain injury. Front. Neurol. 13:897454. 10.3389/fneur.2022.897454 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

