Flavonoids from Clerodendrum genus and their biological activities
- PMID: 39713250
- PMCID: PMC11661801
- DOI: 10.5599/admet.2442
Flavonoids from Clerodendrum genus and their biological activities
Abstract
Background and purpose: Many studies have been performed to identify new sources, their optimal isolation, and the biological activities of flavonoids due to nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, and cosmeceutical properties.
Experimental approach: This review describes the method for flavonoid isolation and characteristic from the Clerodendrum genus and their biological activities with the indication of the most active ones. To perform a comprehensive review, a thorough literature review using Google Scholar, Scopus, and Science Direct was performed with keyword alone or in combination with other words.
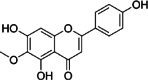
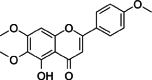
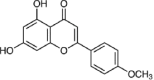
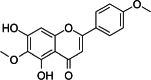
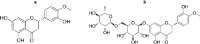
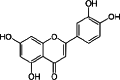
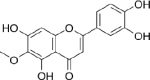
Key results: The isolation and identification of flavonoids from the Clerodendrum genus have revealed a variety of compounds using various methods. Various studies conducted in vivo, in vitro and in silico also reported bioactivities of these flavonoids.
Conclusion: Several factors determine the flavonoid content in the Clerodendrum genus, among others, the different parts of the plant, extraction techniques, and solvent combination used. Isolated flavonoids also show significant biological activities, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobials, antidiabetic, anticancer, anti-tyrosinase, and neuroprotective agents.
Keywords: Traditional medicine; bioactivities; isolation; secondary metabolites.
Copyright © 2024 by the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest statement: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
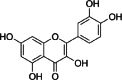
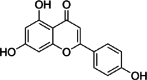
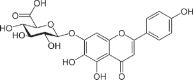
Similar articles
-
Biologically Active Diterpenoids in the Clerodendrum Genus-A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 20;23(19):11001. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911001. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional uses and pharmacological properties of Clerodendrum phytochemicals.J Tradit Complement Med. 2017 May 11;8(1):24-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.04.001. eCollection 2018 Jan. J Tradit Complement Med. 2017. PMID: 29321986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clerodendrum serratum (L.) Moon. - a review on traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological activities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Jun 11;154(2):268-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.03.071. Epub 2014 Apr 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24727551 Review.
-
Traditional uses, chemical diversity and biological activities of Panax L. (Araliaceae): A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Dec 5;263:112792. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112792. Epub 2020 Apr 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32311488 Review.
-
UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS Based Identification, Quantification, and Assessment of in Silico Molecular Interactions of Major Phytochemicals from Bioactive Fractions of Clerodendrum glandulosum Lindl. Leaves.Chem Biodivers. 2022 Oct;19(10):e202200617. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202200617. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Chem Biodivers. 2022. PMID: 36106373
References
-
- Erukainure O.L., Oke O. V., Ajiboye A.J., Okafor O.Y.. Nutritional qualities and phytochemical constituents of Clerodendrum volubile, a tropical non-conventional vegetable. International Food Research Journal 18 (2011) 1393-1399. http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my/18%20(04)%202011/(27)IFRJ-2011-009.pdf
-
- Shrivastava N., Patel T.. Clerodendrum and Heathcare: An Overview. Medicinal and Aromatic Plant Science and Biotechnology ©2007 Global Science Books 1 (2007) 142-150. http://www.globalsciencebooks.info/Online/GSBOnline/images/0706/MAPSB_1(...
-
- Kar P., Goyal A.K., Das A.P., Sen A.. Antioxidant and pharmaceutical potential of Clerodendrum L.: An overview. International Journal of Green Pharmacy 8 (2014). 210-216. https://www.greenpharmacy.info/index.php/ijgp/article/view/415
-
- Yadav A., Kuamr V.P., Chand T., Bora R.H.. Ethno-medicinal knowledge of Clerodendrum L. among different tribes of Nambor reserve forest, Assam, India. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry 7 (2018). 1567-1570. https://www.phytojournal.com/archives/2018/vol7issue5/PartAA/7-5-235-900...
-
- Rueda R.M.. The Genus Clerodendrum (Verbenaceae) in Mesoamerica. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden 80 (1993) 870-890. https://doi.org/10.2307/2399934 10.2307/2399934 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
