Basil seed mucilage as a bioadhesive polymer: Development of naproxen sodium microspheres and suppositories with in-vitro and ex-vivo studies
- PMID: 39713257
- PMCID: PMC11661803
- DOI: 10.5599/admet.2372
Basil seed mucilage as a bioadhesive polymer: Development of naproxen sodium microspheres and suppositories with in-vitro and ex-vivo studies
Abstract
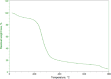
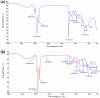
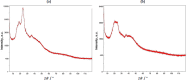
Background and purpose: The study explores basil seed mucilage as a bioadhesive carrier for naproxen sodium, demonstrating its ability to enhance solubility when administered rectally. The mucilage, derived from Ocimum basilicum seeds, showed bioadhesive properties and thermal stability, as confirmed by FTIR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction analysis.
Experimental approach: Microspheres were prepared using a double emulsion solvent evaporation technique, varying polymer ratios to optimize drug delivery.
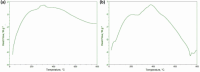
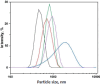
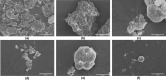
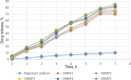
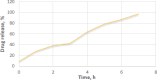
Key results: Particle size analysis revealed a range of 456±0.51 to 712±0.21 μm, with larger microspheres formed at higher mucilage concentrations due to increased viscosity. Encapsulation efficiency ranged from 45.01±0.25 % to 79.4±0.93 %, improving with higher basil/alginate ratios. The superior batch, OBM5, showed excellent mucoadhesive qualities in ex-vivo assays, attributed to the increased polymer content, facilitating interaction with rectal mucosa. SEM analysis of OBM5 indicated a spherical, monolithic structure conducive to free flow. Drug release was efficient, with OBM5 achieving 88.7±1.3 % after 7 hours, indicating a controlled release profile.
Conclusion: Incorporated into polyethylene glycol (PEG) 4000 suppositories, supposetories were completely disintegrated in buffer solution within 25 minutes. The bioadhesive force of basil seed mucilage on rectal mucosa was significantly enhanced, reaching 6.44±0.58 g, correlating with mucilage concentration. These findings underscore the efficacy of basil seed mucilage as a bioadhesive biopolymer for rectal drug delivery systems.
Keywords: Ocimum basilicum; bioadhesive; colorectal administration; drug delivery; drug solubility; mucilage.
Copyright © 2024 by the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and evaluation of sodium alginate-basil seeds mucilage beads as a suitable carrier for controlled release of metformin.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Sep 15;159:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.111. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32330501
-
Basil seed mucilage as a new source for electrospinning: Production and physicochemical characterization.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Feb;95:689-695. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.11.116. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 27919814
-
Synthesis and characterization of basil seed mucilage coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as a drug carrier for the controlled delivery of cephalexin.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Jul 1;113:317-328. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.134. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29481957
-
Development, modification and characterization of new biodegradable film from basil seed (Ocimum basilicum L.) mucilage.J Sci Food Agric. 2019 Sep;99(12):5508-5515. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9812. Epub 2019 Jun 13. J Sci Food Agric. 2019. PMID: 31099416
-
Application of seed mucilage as functional biopolymer in meat product processing and preservation.Carbohydr Polym. 2024 Sep 1;339:122228. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.122228. Epub 2024 May 1. Carbohydr Polym. 2024. PMID: 38823903 Review.
References
-
- Guru P.R., Kar R.K., Nayak A.K., Mohapatra S. A comprehensive review on pharmaceutical uses of plant-derived biopolysaccharides. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 233 (2023) 123454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123454. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123454 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Acebedo-Martínez F.J., Domínguez-Martín A., Alarcón-Payer C., Sevillano-Páez A., Verdugo-Escamilla C., González-Pérez J.M., Martínez-Checa F., Choquesillo-Lazarte D. Enhanced NSAIDs Solubility in Drug–Drug Formulations with Ciprofloxacin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24 (2023) 3305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043305. 10.3390/ijms24043305 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou D., Barney J.N., Welbaum G.E. Production, composition, and ecological function of sweet-basil-seed mucilage during hydration. Horticulturae 8 (2022) 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8040327 10.3390/horticulturae8040327 - DOI
-
- Tripathi D., Sharma D.K., Sahoo J., Raman S.K. Enhanced Solubility of Meloxicam with Sodium Benzoate Hydrotrope: Ecofriendly Approach for Improved Topical Drug Delivery. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education and Research 56 (2022) 1052-1062. https://doi.org/10.5530/ijper.56.4.186. 10.5530/ijper.56.4.186 - DOI
-
- Kapoor A., Mishra S.K., Verma D.K., Pandey P. Chemical penetration enhancers for transdermal drug delivery system. Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics 8 (2018) 62-66. https://doi.org/10.22270/jddt.v8i5-s.1952. 10.22270/jddt.v8i5-s.1952 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
