This is a preprint.
Perceptual choice and motor signals in mouse somatosensory cortex
- PMID: 39713341
- PMCID: PMC11661076
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.12.06.627272
Perceptual choice and motor signals in mouse somatosensory cortex
Abstract
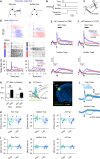
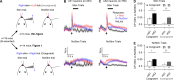
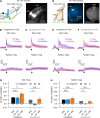
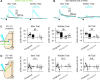
Somatosensory cortex activity relates both to sensation and movement, reflecting their intimate relationship, but the extent and nature of sensory-motor interactions in the somatosensory cortex remain unclear. Here, we investigated perception-related sensory and motor signals in the whisker areas of mouse primary (wS1) and secondary (wS2) somatosensory cortices. We recorded neuronal activity while mice performed a whisker detection task using two alternative lickports, one each to indicate the presence or absence of a whisker deflection on a given trial. One group of mice reported the presence of the whisker stimulus by licking at the port on the same ("congruent") side of the animal as the stimulated whisker, whereas a second group of mice did so by licking at the opposite ("incongruent") side. Activity of single neurons in wS1 and wS2 correlated with perceptual choice. This choice-related activity was enhanced when responding to the congruent side. wS2 neurons projecting along two output pathways-to wS1 or to whisker secondary motor cortex, wM2-also showed choice-related activity, but differed in their dependence on congruence and in the effects of optogenetic manipulation. Thus, somatosensory cortex contains pathway- and action-specific choice-related activity.
Figures
References
-
- Sachidhanandam S., Sreenivasan V., Kyriakatos A., Kremer Y. & Petersen C. C. H. Membrane potential correlates of sensory perception in mouse barrel cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 1671–1677 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Oryshchuk A. et al. Distributed and specific encoding of sensory, motor, and decision information in the mouse neocortex during goal-directed behavior. Cell Rep. 43, 113618 (2024). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
