This is a preprint.
Perivascular Macrophages Convert Physical Wound Signals Into Rapid Vascular Responses
- PMID: 39713421
- PMCID: PMC11661168
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.12.09.627538
Perivascular Macrophages Convert Physical Wound Signals Into Rapid Vascular Responses
Abstract
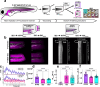
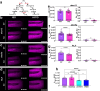
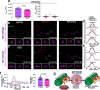
Leukocytes detect distant wounds within seconds to minutes, which is essential for effective pathogen defense, tissue healing, and regeneration. Blood vessels must detect distant wounds just as rapidly to initiate local leukocyte extravasation, but the mechanism behind this immediate vascular response remains unclear. Using high-speed imaging of live zebrafish larvae, we investigated how blood vessels achieve rapid wound detection. We monitored two hallmark vascular responses: vessel dilation and serum exudation. Our experiments-including genetic, pharmacologic, and osmotic perturbations, along with chemogenetic leukocyte depletion-revealed that the cPla2 nuclear shape sensing pathway in perivascular macrophages converts a fast (~50 μm/s) osmotic wound signal into a vessel-permeabilizing, 5-lipoxygenase (Alox5a) derived lipid within seconds of injury. These findings demonstrate that perivascular macrophages act as physicochemical relays, bridging osmotic wound signals and vascular responses. By uncovering this novel type of communication, we provide new insights into the coordination of immune and vascular responses to injury.
Keywords: ER lipid flow; cPla2; epithelial wounding; macrophage; mechanotransduction; nuclear membrane tension; vessel dilation; vessel osmotic surveillance; vessel permeabilization.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests Authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Buffering of nuclear membrane tension and mechanotransduction by the endoplasmic reticulum revealed by quantitative ALPIN imaging.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 9:rs.3.rs-5530637. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5530637/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 39711539 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Myeloid Wls expression is dispensable for skin wound healing and blood vessel regeneration.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 22;13:957833. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.957833. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36082070 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages undergo a behavioural switch during wound healing in zebrafish.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Nov 1;192:200-212. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.09.021. Epub 2022 Sep 24. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 36162743
-
Macrophages in Skin Wounds: Functions and Therapeutic Potential.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 8;12(11):1659. doi: 10.3390/biom12111659. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36359009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
H Vessel Formation as a Marker for Enhanced Bone Healing in Irradiated Distraction Osteogenesis.Semin Plast Surg. 2024 Jan 19;38(1):31-38. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1778039. eCollection 2024 Feb. Semin Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 38495069 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
