Development and Validation of Nomograms to Predict the Overall Survival and Progression-Free Survival in Patients with Advanced Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 39713568
- PMCID: PMC11663373
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S489960
Development and Validation of Nomograms to Predict the Overall Survival and Progression-Free Survival in Patients with Advanced Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to develop and validate clinical nomograms for predicting progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in unresectable ICC patients.
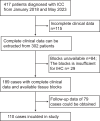
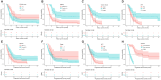
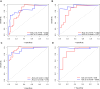
Patients and methods: Patients with ICC between 1 January 2018 and 31 May 2023 were selected and randomized into a training set and an internal validation set as a 7:3 ratio. Data analysis and modeling were conducted through R software. The univariate and multivariate Cox regression models were used to analyze the prognosis factors affecting OS and PFS. Survival analysis was conducted using the Kaplan-Meier (KM) method, and comparisons were made using the Log rank test. Then, two nomogram models were constructed to predict OS and PFS, respectively. The nomogram was evaluated and calibrated using the Harrell's C-index, receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC), and calibration plots, and the decision curve analysis (DCA) was conducted to assess its clinical utility.
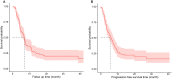
Results: A total of 110 patients were enrolled in this study, with 77 to the training set and 33 to the validation set. In the entire population, the OS rates at 6 and 12 months were 75.5% and 35.5%, respectively, while the PFS rates at 6 and 12 months were 47.3% and 20%, respectively. Cox regression analyses showed that ECOG, Tumor volume, HBsAg and AFP were the prognosis factors of OS, and the predictors in the model of PFS included Gender, Stage of tumor, CDC20 expression and AFP. The nomograms were constructed based on the predictors above. The C-index for predicting OS was 0.802 (0.755, 0.849) in the training set, 0.813 (0.764, 0.862) in the internal validation set; the C-index for predicting PFS was 0.658 (0.568, 0.748) in the training set, and 0.795 (0.705, 0.885) in the internal validation set. Finally, calibration curves and DCA indicated that two nomograms showed favorable performance.
Conclusion: Two practical and effective prognostic nomograms were developed to assist clinicians in evaluating OS and PFS in patients with unresectable ICC.
Keywords: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; nomogram; overall survival; prognostic model; progression-free survival.
© 2024 Xian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Construction of a prognostic model for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer patients undergoing immune therapy in northernmost China and prediction of treatment efficacy based on response status at different time points.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 May 15;150(5):255. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05767-6. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38750370 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of sarcopenia combined with preoperative fibrinogen-albumin ratio in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after surgery: A multicenter, prospective study.Cancer Med. 2021 Jul;10(14):4768-4780. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4035. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34105304 Free PMC article.
-
Nomograms predicting benefit after immunotherapy in oral bifidobacteria supplementation ICC patients: a retrospective study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Oct 14;24(1):1274. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12982-4. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39402531 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic nomograms for newly diagnosed intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with brain metastasis: A population-based analysis.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Sep;247(18):1657-1669. doi: 10.1177/15353702221113828. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 35946168 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of prognostic nomograms for early-onset colon cancer in different tumor locations: a population-based study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Oct 21;23(1):362. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02991-1. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37865754 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prediction of the prognosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients after hepatectomy via propensity score matching: a competitive risk model analysis.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 30;14(3):1884-1901. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1819. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40225005 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

