Systematic Analysis of Disulfidptosis-Related lncRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Vascular Invasion Revealed That AC131009.1 Can Promote HCC Invasion and Metastasis through Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
- PMID: 39713637
- PMCID: PMC11656384
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c09411
Systematic Analysis of Disulfidptosis-Related lncRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Vascular Invasion Revealed That AC131009.1 Can Promote HCC Invasion and Metastasis through Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
Abstract
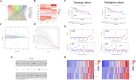
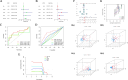
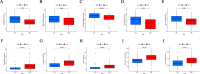
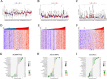
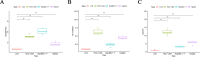
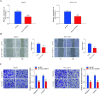
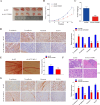
Disulfidptosis, a recently identified pathway of cellular demise, served as the focal point of this research, aiming to pinpoint relevant lncRNAs that differentiate between hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with and without vascular invasion while also forecasting survival rates and responses to immunotherapy in patients with vascular invasion (VI+). First, we identified 300 DRLRs in the TCGA database. Subsequently, utilizing univariate analysis, LASSO-Cox proportional hazards modeling, and multivariate analytical approaches, we selected three DRLRs (AC009779.2, AC131009.1, and LUCAT1) with the highest prognostic value to construct a prognostic risk model for VI+ HCC patients. Multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that this model is an independent prognostic factor for predicting overall survival that outperforms traditional clinicopathological factors. Pathway analysis demonstrated the enrichment of tumor and immune-related pathways in the high-risk group. Immune landscape analysis revealed that immune cell infiltration degrees and immune functions had significant differences. Additionally, we identified valuable chemical drugs (AZD4547, BMS-536924, BPD-00008900, dasatinib, and YK-4-279) for high-risk VI+ HCC patients. In-depth bioinformatics analysis was subsequently conducted to assess immune characteristics, drug susceptibility, and potential biological pathways involving the three hub DRLRs. Furthermore, the abnormally elevated transcriptional levels of the three DRLRs in HCC cell lines were validated through qRT-PCR. Functional cell assays revealed that silencing the expression of lncRNA AC131009.1 can inhibit the migratory and invasive capabilities of HCC cells, a finding further corroborated by the chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay. Immunohistochemical analysis and hematoxylin-eosin staining (HE) staining provided preliminary evidence that AC131009.1 may promote the invasion and metastasis of HCC cells by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in both subcutaneous xenograft models and orthotopic HCC models within nude mice. To summarize, we developed a risk assessment model founded on DRLRs and explored the potential mechanisms by which hub DRLRs promote HCC invasion and metastasis.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
