Metal-Free Synthesis of Functionalized Indolizines via a Cascade Michael/SN2/Aromatization Reaction of 2-Alkylazaarene Derivatives with Bromonitroolefins
- PMID: 39713660
- PMCID: PMC11656401
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c09295
Metal-Free Synthesis of Functionalized Indolizines via a Cascade Michael/SN2/Aromatization Reaction of 2-Alkylazaarene Derivatives with Bromonitroolefins
Abstract
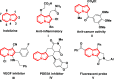
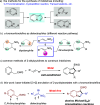
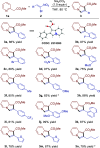
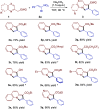
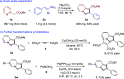
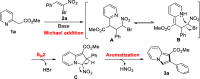
A transition metal-free domino Michael/SN2/aromatization annulation of 2-pyridylacetates with bromonitroolefins has been developed. A wide range of substrates containing various substituted groups was compatible with the present methodology and afforded functionalized indolizines with moderate to excellent yield (up to 99% yield). In addition, the potential practicality of the method stood out through scale-up reactions and further transformations to other valuable compounds. In our view, this study is an essential complement for the rapid construction of indolizine derivatives through a metal-free strategy.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthesis of functionalized indolizines via gold(i)-catalyzed intramolecular hydroarylation/aromatization of pyrrole-ynes.Org Biomol Chem. 2017 Oct 4;15(38):8119-8133. doi: 10.1039/c7ob02102j. Org Biomol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28905974
-
B2pin2-Mediated Cascade Cyclization/Aromatization Reaction: Facial Access to Functionalized Indolizines.Org Lett. 2022 Oct 14;24(40):7372-7377. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c02905. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Org Lett. 2022. PMID: 36173232
-
Synthesis of Highly Functionalized Indolizines via NIS-Promoted Spiroannulation/Ring-Opening Aromatization of Alkylidene Oxindoles with 2-(Pyridin-2-yl)acetate Derivatives.J Org Chem. 2025 Mar 21;90(11):4046-4053. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5c00026. Epub 2025 Mar 10. J Org Chem. 2025. PMID: 40062558
-
Recent Advances on the Construction of Functionalized Indolizine and Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine Derivatives.Chem Rec. 2024 Dec;24(12):e202400135. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202400135. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Chem Rec. 2024. PMID: 39439190 Review.
-
Development of cascade reactions for the concise construction of diverse heterocyclic architectures.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Aug 21;45(8):1278-93. doi: 10.1021/ar200338s. Epub 2012 May 11. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22577988 Review.
References
-
-
For selected reviews, see:
- Heravi M. M.; Zadsirjan V. Prescribed drugs containing nitrogen heterocycles: an overview. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 44247–44311. 10.1039/D0RA09198G. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Obaid R. J.; Mughal E. U.; Naeem N.; Al-Rooqi M. M.; Sadiq A.; Jassas R. S.; Moussa Z.; Ahmed S. A. Pharmacological significance of nitrogen-containing five and six-membered heterocyclic scaffolds as potent cholinesterase inhibitors for drug discovery. Process Biochem. 2022, 120, 250–259. 10.1016/j.procbio.2022.06.009. - DOI
- Kumar A.; Singh A. K.; Singh H.; Vijayan V.; Kumar D.; Naik J.; Thareja S.; Yadav J. P.; Pathak P.; Grishina M.; Verma A.; Khalilullah H.; Jaremko M.; Emwas A. H.; Kumar P. Nitrogen Containing Heterocycles as Anticancer Agents: A Medicinal Chemistry Perspective. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 299.10.3390/ph16020299. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
-
- Hagishita S.; Yamada M.; Shirahase K.; Okada T.; Murakami Y.; Ito Y.; Matsuura T.; Wada M.; Kato T.; Ueno M.; Chikazawa Y.; Yamada K.; Ono T.; Teshirogi I.; Ohtani M. Potent Inhibitors of Secretory Phospholipase A2: Synthesis and Inhibitory Activities of Indolizine and Indene Derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 3636–3658. 10.1021/jm960395q. - DOI - PubMed
- Dennis E. A.; Cao J.; Hsu Y.-H.; Magrioti V.; Kokotos G. Phospholipase A2 Enzymes: Physical Structure, Biological Function, Disease Implication, Chemical Inhibition, and Therapeutic Intervention. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6130–6185. 10.1021/cr200085w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Sharma V.; Kumar V. Indolizine: a biologically active moiety. Med. Chem. Res. 2014, 23, 3593–3606. 10.1007/s00044-014-0940-1. - DOI
-
- Ghinet A.; Abuhaie C. M.; Gautret P.; Rigo B.; Dubois J.; Farce A.; Belei D.; Bîcu E. Studies on indolizines. Evaluation of their biological properties as microtubule-interacting agents and as melanoma targeting compounds. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 115–127. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.10.041. - DOI - PubMed
- Moon S.-H.; Jung Y.; Kim S. H.; Kim Y. Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of anti-cancer indolizine derivatives via inhibiting β-catenin activity and activating p53. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 110–113. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.11.021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sharma P.; Kumar A.; Sharma S.; Rane N. Studies on synthesis and evaluation of quantitative structure–activity relationship of 5-[(3′-chloro-4′,4′-disubstituted-2-oxoazetidinyl)(N-nitro)amino]-6-hydroxy-3-alkyl/aryl[1,3]aza-phospholo[1,5-a]pyridinyl phosphorus dichlorides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 937–943. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.12.050. - DOI - PubMed
- Bedjeguelal K.; Bienayme H.; Dumoulin A.; Poigny S.; Schmitt P.; Tam E. Discovery of protein–protein binding disruptors using multi-component condensations small molecules. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 3998–4001. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.05.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen S.; Xia Z.; Nagai M.; Lu R.; Kostik E.; Przewloka T.; Song M.; Chimmanamada D.; James D.; Zhang S.; Jiang J.; Ono M.; Koya K.; Sun L. Novel indolizine compounds as potent inhibitors of phosphodiesterase IV (PDE4): structure–activity relationship. MedChemComm 2011, 2, 176–180. 10.1039/C0MD00215A. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
