Innovative Approach to Sustainable Fertilizer Production: Leveraging Electrically Assisted Conversion of Sewage Sludge for Nutrient Recovery
- PMID: 39713698
- PMCID: PMC11656355
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c07926
Innovative Approach to Sustainable Fertilizer Production: Leveraging Electrically Assisted Conversion of Sewage Sludge for Nutrient Recovery
Abstract
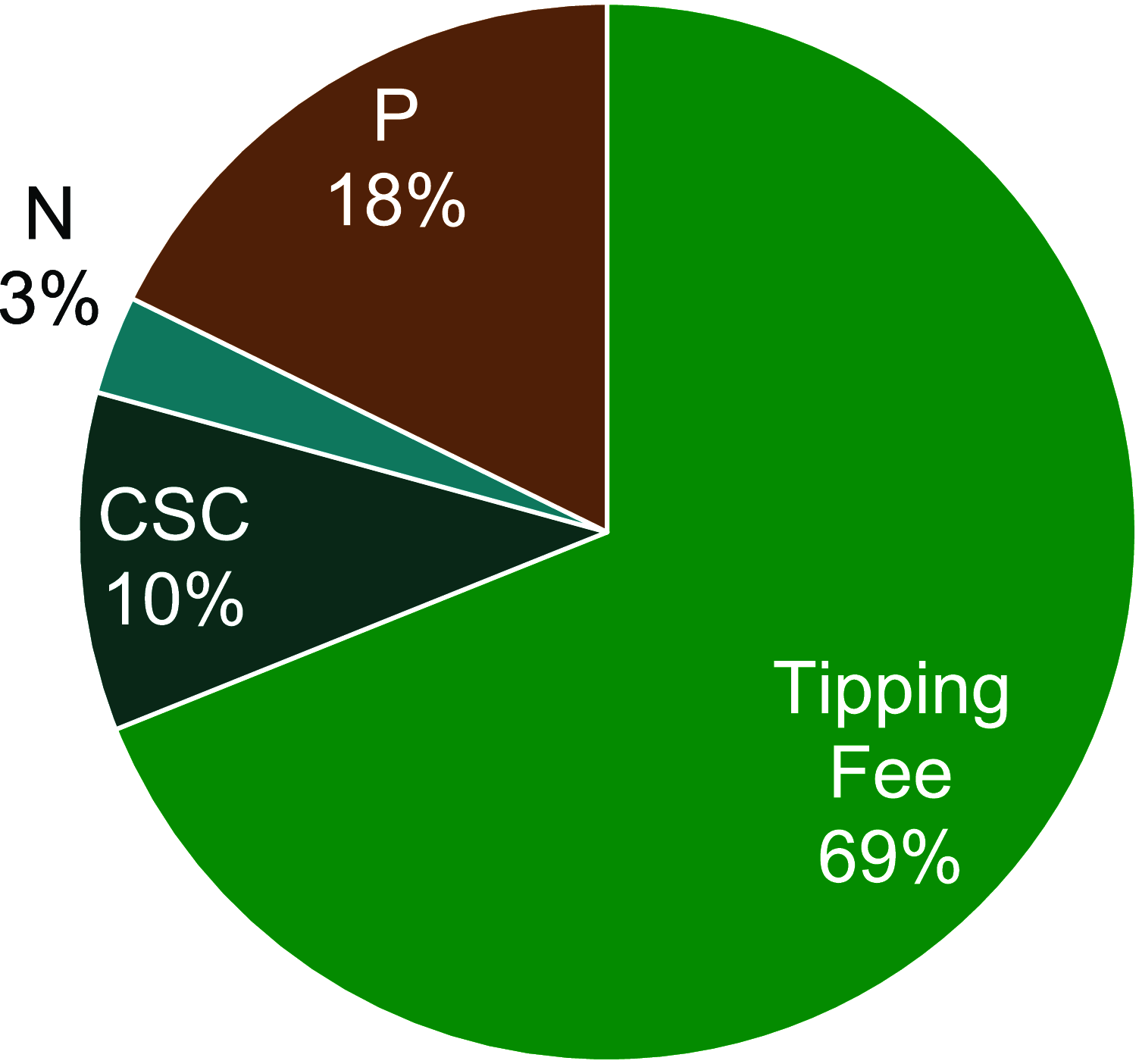
Efforts addressing sludge management, food security, and resource recovery have led to novel approaches in these areas. Electrically assisted conversion of sludge stands out as a promising technology for sewage sludge valorization, producing nitrogen and phosphorus-based fertilizers. The adoption of this technology, which could lead to a fertilizer circular economy, holds the potential to catalyze a transformative change in wastewater treatment facilities toward process intensification, innovation, and sustainability. This paper provides insights into the economic aspects of the technology, policy considerations, and challenges involved in realizing the potential of electrified processes for sludge valorization. To demonstrate the impact of the technology, a case study for its implementation in the United States assuming the municipal wastewater treatment plants market is discussed. It was found that electrically assisted sludge conversion could enable the recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus from waste, representing up to 9% of the nitrogen and 32% of the phosphorus consumption of the U.S. for fertilizer use. This technology also enables full electrification and modularization of the process, thereby presenting significant economic and environmental opportunities.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Botte, G. G. is the inventor of the U.S. Pending Patent Application "Methods and Systems for the Electrocatalysis of Municipal Sludge and Biosolids", No. 63/506,601 (2023).
Figures



References
-
- Turovskiy I. S.; Mathai P. K.. Wastewater Sludge Processing; Wiley Interscience: Hoboken, N.J, 2006.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
