Study on the Mechanism of UMI-77 in the Treatment of Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury Based on Transcriptomics and Metabolomics
- PMID: 39713715
- PMCID: PMC11663390
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S495512
Study on the Mechanism of UMI-77 in the Treatment of Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury Based on Transcriptomics and Metabolomics
Abstract
Introduction: Sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI), a critical sequela of systemic inflammation, often progresses to acute respiratory distress syndrome, conferring high mortality. Although UMI-77 has demonstrated efficacy in mitigating lung injury in sepsis, the molecular mechanisms underlying its action have not yet been fully elucidated.
Methods: This study aimed to delineate the mechanism by which UMI-77 counteracts sepsis-induced ALI using comprehensive transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses.
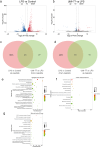
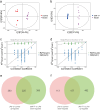
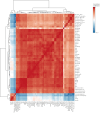
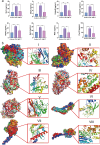
Results: UMI-77 significantly ameliorated histopathological changes in the lungs of mice with sepsis-induced ALI Transcriptomic analysis revealed that 124 differentially expressed genes were modulated by UMI-77 and were predominantly implicated in chemokine-mediated signaling pathways, apoptosis regulation, and inflammatory responses. Integrated metabolomic analysis identified Atp4a, Ido1, Ctla4, and Cxcl10 as key genes, and inosine 5'-monophosphate (IMP), thiamine monophosphate, thymidine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (dTMP) as key differential metabolites. UMI-77 may regulate key genes (Atp4a, Ido1, Ctla4, and Cxcl10) to affect key metabolites (IMP, thiamine monophosphate, and dTMP) and their target genes (Entpd2, Entpd1, Nt5e, and Hprt) involved in cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, gastric acid secretion, pyrimidine, and purine metabolism in the treatment of sepsis-induced ALI.
Conclusion: UMI-77 exerts its therapeutic effect in sepsis-induced ALI through intricate modulation of pivotal genes and metabolites, thereby influencing critical biological pathways. This study lays the groundwork for further development and clinical translation of UMI-77 as a potential therapeutic agent for sepsis-associated lung injuries.
Keywords: cytokine signaling; genes; inflammation; metabolites; sepsis-induced ALI.
© 2024 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
S100A9 exacerbates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via the IL17-NFκB-caspase-3 signaling pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 May 28;710:149832. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.149832. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38588614
-
Naringin dihydrochalcone alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via improving gut microbial homeostasis and activating GPR18 receptor.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Aug 20;137:112418. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112418. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38901244
-
Network Pharmacology Analysis of the Therapeutic Potential of Colchicine in Acute Lung Injury.Int J Clin Pract. 2024 Feb 6;2024:9940182. doi: 10.1155/2024/9940182. eCollection 2024. Int J Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 38352962 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of glucose metabolism on inflammatory processes in sepsis-induced acute lung injury.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 6;15:1508985. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1508985. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39712019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of inflammatory lung injury and repair by metabolic signaling in endothelial cells.Curr Opin Hematol. 2025 May 1;32(3):157-167. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000848. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Curr Opin Hematol. 2025. PMID: 39450949 Review.
Cited by
-
Methyltransferase ZC3H13 regulates ferroptosis of alveolar macrophages in sepsis-associated acute lung injury via PRDX6/p53/SLC7A11 axis.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Jul 12;25(1):156. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01659-1. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40646387
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

