Changes in PD-1 expression on T lymphocyte subsets and related immune indicators before and after definitive chemoradiotherapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 39713872
- PMCID: PMC11703528
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2445190
Changes in PD-1 expression on T lymphocyte subsets and related immune indicators before and after definitive chemoradiotherapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to observe the dynamic changes in the expression of T lymphocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, and PD-1 in patients with first-diagnosed esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) before and after chemoradiotherapy (CRT) and evaluate the impact of PD-1 expression in peripheral blood on the short-term outcome of patients with ESCC.
Patients and methods: Seventy-three patients with ESCC who were treated with definitive CRT were enrolled. Before and after CRT, flow cytometry was used to detect thePD-1 expression in the peripheral blood and related immune indicators. Peripheral blood from 10 healthy individuals was used as control.
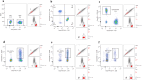
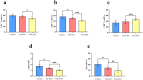
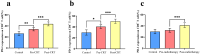
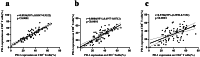
Results: The percentages of CD3+ (p = 0.018), CD4+ (p < 0.001), and CD8+ T cells (p < 0.001); NK cells (p = 0.009); and the CD4+/CD8+ ratio (p < 0.001), as well as PD-1+CD3+ (p < 0.001), PD-1+CD4+ (p < 0.001), and PD-1+CD8+ (p < 0.001) T cells, before CRT significantly differed from those in the post-CRT group. The percentages of PD-1+CD8+ T cells differed significantly between the radiotherapy alone and CRT groups (p < 0.05). PD-1 expression in CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells significantly decreased in patients achieving overall response rate (all p < 0.05). Compared with those in the incomplete response group, PD-1+CD8+ T cells significantly decreased in the CR group (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: CRT aggravated immunosuppression and increased PD-1 expression in T lymphocyte subsets in patients with ESCC, possibly related to the radiation field. PD-1 expression in T lymphocyte subsets can predict short-term outcomes in patients and provide a theoretical basis for the sequential application of PD-1 immunosuppressants after radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Keywords: NK cells; PD-1; T lymphocyte subsets; chemoradiotherapy; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; immunotherapy.
Plain language summary
Chemoradiotherapy (CRT) reduced the overall immune function of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), and the degree of decline was related to the irradiation area.PD-1 expression in T lymphocytes increased considerably after CRT, suggesting that the sequential application of PD-1 immunosuppressants after radiotherapy and chemotherapy can be beneficial.PD-1 expression on T lymphocytes may serve as a potential indicator for predicting the short-term outcomes of ESCC.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
