Association of APOE alleles and polygenic profiles comprising APOE-TOMM40-APOC1 variants with Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging markers
- PMID: 39713891
- PMCID: PMC11848341
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14445
Association of APOE alleles and polygenic profiles comprising APOE-TOMM40-APOC1 variants with Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging markers
Abstract
Introduction: TOMM40 and APOC1 variants can modulate the APOE-ε4-related Alzheimer's disease (AD) risk by up to fourfold. We aim to investigate whether the genetic modulation of ε4-related AD risk is reflected in brain morphology.
Methods: We tested whether 27 magnetic resonance imaging-derived neuroimaging markers of neurodegeneration (volume and thickness in temporo-limbic regions) are associated with APOE-TOMM40-APOC1 polygenic profiles using the National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center Uniform Data Set linked to the AD Genetic Consortium data.
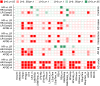
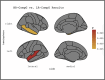
Results: All brain regions studied using structural phenotypes were smaller in individuals with AD. The ε4 allele was associated with smaller limbic (entorhinal, hippocampus, parahippocampus) brain volume and cortical thickness in AD cases than controls. There were significant differences in the associations for the higher-risk and lower-risk ε4-bearing APOE-TOMM40-APOC1 profiles with temporo-limbic region markers.
Discussion: The APOE-AD heterogeneity may be partly attributed to the modulating role of the TOMM40 and APOC1 genes in the APOE cluster.
Highlights: The ε4 allele is associated with smaller values of neuroimaging markers in AD cases. Larger values of neuroimaging markers may protect against AD in the ε4 carriers. TOMM40 and APOC1 variants differentiate AD risk in the ε4 carriers. The same variants can differentiate the links between ε4 and neuroimaging markers.
Keywords: APOE locus; Alzheimer's disease; neuroimaging markers; polygenic profiles.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Associations of the APOE ε2 and ε4 alleles and polygenic profiles comprising APOE-TOMM40-APOC1 variants with Alzheimer's disease biomarkers.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Nov 17;14(24):9782-9804. doi: 10.18632/aging.204384. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 36399096 Free PMC article.
-
Definitive roles of TOMM40-APOE-APOC1 variants in the Alzheimer's risk.Neurobiol Aging. 2022 Feb;110:122-131. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2021.09.009. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Neurobiol Aging. 2022. PMID: 34625307 Free PMC article.
-
TOMM40 and APOE variants synergistically increase the risk of Alzheimer's disease in a Chinese population.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021 Jun;33(6):1667-1675. doi: 10.1007/s40520-020-01661-6. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 32725468
-
Hippocampal atrophy and apolipoprotein E genotype are independently associated with Alzheimer's disease.Ann Neurol. 1998 Mar;43(3):303-10. doi: 10.1002/ana.410430307. Ann Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9506546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging studies and APOE genotype in persons at risk for Alzheimer's disease.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2006 Feb;8(1):11-7. doi: 10.1007/s11920-006-0076-1. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2006. PMID: 16513038 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Haplotype-Resolved DNA Methylation at the APOE Locus identifies Allele-Specific Epigenetic Signatures Relevant to Alzheimer's Disease Risk.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 2:2025.07.01.662592. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.01.662592. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40631171 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Development of a machine learning-based predictive risk model combining fatty acid metabolism and ferroptosis for immunotherapy response and prognosis in prostate cancer.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 13;16(1):744. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02484-5. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40355680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lescai F, Chiamenti AM, Codemo A, et al. An APOE haplotype associated with decreased epsilon4 expression increases the risk of late onset Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;24:235‐245. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20 AG068053/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG068057/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- University of Kansas Alzheimer's Disease Research Center
- P30 AG066509/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068077/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002366/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072979/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068082/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072975/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Duke University
- P30 AG066507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072946/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066518/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20GM130423/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066511/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG072122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066512/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG072973/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066515/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG047310/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5UL1TR002366/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066508/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072978/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066519/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG061853/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG074855/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072973/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062422/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG079280/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG041689/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066462/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG065477/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066530/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Alzheimer's Disease Genetics Consortium
- R01 AG070488/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG059716/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM130423/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072977/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062677/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG070488/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068024/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072958/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062715/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066506/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066468/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG065477/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072947/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072931/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG047310/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- National Institute on Aging Genetics of Alzheimer's Disease
- P30 AG066514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072959/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061853/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

