Clinical Characteristics and Genotype-phenotype Correlation in Turkish Patients with a Diagnosis of Resistance to Thyroid Hormone Beta
- PMID: 39713907
- PMCID: PMC12118323
- DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2024.2024-8-14
Clinical Characteristics and Genotype-phenotype Correlation in Turkish Patients with a Diagnosis of Resistance to Thyroid Hormone Beta
Abstract
Objective: Resistance to thyroid hormone beta (RTHβ) is a rare disorder characterized by a fairly heterogeneous clinical presentation due to varying degrees of tissue response to thyroid hormone. The present study aimed to evaluate the clinical and laboratory features and genotype-phenotype relationship of Turkish patients with RTHβ.
Methods: Patients who underwent a THRβ gene analysis between September 2019 and September 2023 were retrospectively reviewed.
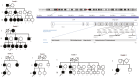
Results: Fifty patients with the clinical features of RTHβ syndrome or a family history of an index case were included. A total of eight different heterozygous pathogenic/likely pathogenic missense variants, three of which were novel, were detected in THRB in 30 patients from 8 unrelated families. Although most patients with RTHβ were asymptomatic, seven patients exhibited various symptoms. Moreover, seven patients had received various treatments before diagnosis. Thyroid autoantibody was positive in 23% of all cases with a variant, and goitre was detected in 56% of children with a variant. While thyroid nodules were detected in seven adult patients, two adults had been diagnosed with papillary thyroid cancer. One child had attention-deficit disorder, learning disability, and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Of the 20 patients without a variant, TSHoma was detected in one.
Conclusion: The present study provides an overview of clinical and genetic characteristics of patients with genetically confirmed RTHβ and expanded the THRB gene variant database with three novel variants. Although most patients with RTHβ are asymptomatic, molecular genetic analysis of the THRB gene and regular follow-up because of the apparent risk of concurrent autoimmune diseases or thyroid cancer is warranted.
Keywords: THRB gene; Thyroid hormones; resistance to thyroid hormone; autoimmune thyroid disease; goitre.
©Copyright 2025 by Turkish Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes / The Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology published by Galenos Publishing House.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutational Landscape of Resistance to Thyroid Hormone Beta (RTHβ).Mol Diagn Ther. 2019 Jun;23(3):353-368. doi: 10.1007/s40291-019-00399-w. Mol Diagn Ther. 2019. PMID: 30976996 Review.
-
Thyroid hormone resistance from newborns to adults: a Spanish experience.J Endocrinol Invest. 2019 Aug;42(8):941-949. doi: 10.1007/s40618-019-1007-4. Epub 2019 Feb 1. J Endocrinol Invest. 2019. PMID: 30707410
-
Autoimmune thyroid disease and thyroid function test fluctuations in patients with resistance to thyroid hormone.Eur J Endocrinol. 2021 Dec 2;186(1):73-82. doi: 10.1530/EJE-21-0584. Eur J Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34727089
-
Clinically Symptomatic Resistance to Thyroid Hormone β Syndrome Because of THRB Gene Mosaicism.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Aug 18;107(9):e3548-e3552. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac347. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35689814
-
Human Genetics of Thyroid Hormone Receptor Beta: Resistance to Thyroid Hormone Beta (RTHβ).Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1801:225-240. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7902-8_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29892828 Review.
References
-
- Dumitrescu AM, Korwutthikulrangsri M, Refetof S. Impaired sensitivity to thyroid hormone: defects of transport, metabolism, and action. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, et al., editors. Endotext. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc. Copyright©2000-2023, MDText.com, Inc.; 2000. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK285557/?report=reader - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
