Basement membranes are crucial for proper olfactory placode shape, position and boundary with the brain, and for olfactory axon development
- PMID: 39713923
- PMCID: PMC11666240
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.92004
Basement membranes are crucial for proper olfactory placode shape, position and boundary with the brain, and for olfactory axon development
Abstract
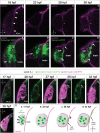
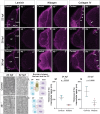
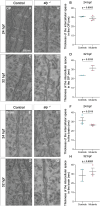
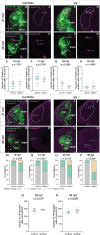
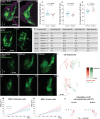
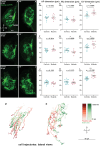
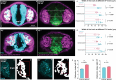
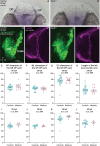
Despite recent progress, the complex roles played by the extracellular matrix in development and disease are still far from being fully understood. Here, we took advantage of the zebrafish sly mutation which affects Laminin γ1, a major component of basement membranes, to explore its role in the development of the olfactory system. Following a detailed characterisation of Laminin distribution in the developing olfactory circuit, we analysed basement membrane integrity, olfactory placode and brain morphogenesis, and olfactory axon development in sly mutants, using a combination of immunochemistry, electron microscopy and quantitative live imaging of cell movements and axon behaviours. Our results point to an original and dual contribution of Laminin γ1-dependent basement membranes in organising the border between the olfactory placode and the adjacent brain: they maintain placode shape and position in the face of major brain morphogenetic movements, they establish a robust physical barrier between the two tissues while at the same time allowing the local entry of the sensory axons into the brain and their navigation towards the olfactory bulb. This work thus identifies key roles of Laminin γ1-dependent basement membranes in neuronal tissue morphogenesis and axon development in vivo.
Keywords: axon; basement membrane; developmental biology; extracellular matrix; morphogenesis; olfactory; placode; zebrafish.
© 2023, Tignard et al.
Conflict of interest statement
PT, KP, AG, MD, MC, CF, ML, JF, MR, SA, AT, MB No competing interests declared, FD Reviewing editor, eLife
Figures




Update of
-
Laminin γ1-dependent basement membranes are instrumental to ensure proper olfactory placode shape, position and boundary with the brain, as well as olfactory axon development.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 29:2023.06.29.547040. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.29.547040. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Dec 23;12:RP92004. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92004. PMID: 39253416 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Laminin γ1-dependent basement membranes are instrumental to ensure proper olfactory placode shape, position and boundary with the brain, as well as olfactory axon development.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 29:2023.06.29.547040. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.29.547040. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Dec 23;12:RP92004. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92004. PMID: 39253416 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Extrinsic mechanical forces mediate retrograde axon extension in a developing neuronal circuit.Nat Commun. 2017 Aug 17;8(1):282. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00283-3. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28819208 Free PMC article.
-
Intertissue mechanical interactions shape the olfactory circuit in zebrafish.EMBO Rep. 2022 Feb 3;23(2):e52963. doi: 10.15252/embr.202152963. Epub 2021 Dec 9. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 34889034 Free PMC article.
-
Functional development of the olfactory system in zebrafish.Mech Dev. 2013 Jun-Aug;130(6-8):336-46. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2012.09.001. Epub 2012 Sep 23. Mech Dev. 2013. PMID: 23010553 Review.
-
Role of laminin-nidogen complexes in basement membrane formation during embryonic development.Experientia. 1995 Sep 29;51(9-10):901-13. doi: 10.1007/BF01921740. Experientia. 1995. PMID: 7556571 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

