SIRT5-mediated HOXA5 desuccinylation inhibits ferroptosis to alleviate sepsis induced-lung injury
- PMID: 39713961
- PMCID: PMC11724168
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12921
SIRT5-mediated HOXA5 desuccinylation inhibits ferroptosis to alleviate sepsis induced-lung injury
Abstract
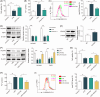
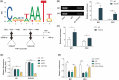
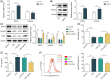
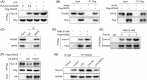
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a common and severe complication of sepsis with a high mortality rate. Ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of cell death, contributes to lung injury. Homeobox A5 (HOXA5) is involved in the regulation of septic acute kidney damage; however, its function on ferroptosis in septic ALI remains unclear. An in vitro model of septic lung injury was established in the pulmonary epithelial cell line (MLE-12) via lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation. Cell viability, ferrous iron (Fe2+) level, and cellular lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS) were determined with Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, iron assay kit, and BODIPY™ 665/676 molecular probe, respectively. HOXA5, ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1), sirtuin 5 (SIRT5), and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) expressions were measured using western blotting and Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase reporter assays were performed to validate HOXA5 binding to the FSP1/GPX4 promoter, and regulation of SIRT5 on HOXA5 desuccinylation was confirmed through co-immunoprecipitation. LPS stimulation induced ferroptosis (reduced cell viability, elevated Fe2+ and lipid ROS levels, and decreased GPX4 levels) and downregulated FSP1 and HOXA5 protein levels. HOXA5 overexpression neutralized LPS-induced ferroptosis. Moreover, LPS exposure inhibited HOXA5 binding to the FSP1 promoter, which was counteracted via HOXA5 overexpression. Furthermore, SIRT5 overexpression suppressed LPS-induced ferroptosis. In LPS-challenged MLE-12 cells, SIRT5-mediated HOXA5 desuccinylation was reduced. HOXA5 depletion neutralized the suppressive role of SIRT5 overexpression in LPS-induced ferroptosis. SIRT5-mediated HOXA5 desuccinylation inhibited LPS-induced ferroptosis by upregulating FSP1, which may offer a prospective therapeutic strategy for septic lung injury.
Keywords: HOXA5; SIRT5; desuccinylation; ferroptosis; sepsis‐induced lung injury.
© 2024 The Author(s). The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates hyperoxia-aggravated septic lung injury via the GPx4-mediated anti-ferroptosis signaling pathway in alveolar epithelial cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2025 Jul;234:86-99. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2025.04.021. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Free Radic Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40246251
-
Isoginkgetin inhibits macrophage activation and ferroptosis of lung epithelial cells under lipopolysaccharide-induced immunological stress via HOXA5-dependent inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κΒ signaling pathway.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2025 Sep;502:117413. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2025.117413. Epub 2025 May 25. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40425070
-
HMGB1 inhibition blocks ferroptosis and oxidative stress to ameliorate sepsis-induced acute lung injury by activating the Nrf2 pathway.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2024 Aug;40(8):710-721. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12851. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38837857 Free PMC article.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 drives epithelial cells ferroptosis in influenza-induced acute lung injury.Redox Biol. 2025 Apr;81:103572. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103572. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 40023977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk Between Sickle Cell Disease and Ferroptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 13;26(8):3675. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083675. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332185 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SIRT5 Inhibits Mitophagy and Inflammation of Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension by Regulating the Desuccinylation of PDK1.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 1. doi: 10.1007/s12033-025-01430-8. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40169475
-
Co-Expression Analysis of the ZDHHC19 Palmitoyltransferase-miR-4733-miR-596 Putative Regulatory Axis in Sepsis.Genes (Basel). 2025 Mar 21;16(4):359. doi: 10.3390/genes16040359. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282319 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

