Enhancing Gene Delivery to Breast Cancer with Highly Efficient siRNA Loading and pH-Responsive Small Extracellular Vesicles
- PMID: 39713992
- PMCID: PMC12067483
- DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.4c01595
Enhancing Gene Delivery to Breast Cancer with Highly Efficient siRNA Loading and pH-Responsive Small Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
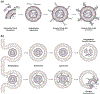
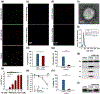
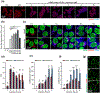
Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) are promising nanocarriers for drug delivery to treat a wide range of diseases due to their natural origin and innate homing properties. However, suboptimal therapeutic effects, attributed to ineffective targeting, limited lysosomal escape, and insufficient delivery, remain challenges in effectively delivering therapeutic cargo. Despite advances in sEV-based drug delivery systems, conventional approaches need improvement to address low drug-loading efficiency and to develop surface functionalization techniques for precise targeting of cells of interest, all while preserving the membrane integrity of sEVs. We report an enhanced gene delivery system using multifunctional sEVs for highly efficient siRNA loading and delivery. The integration of chiral graphene quantum dots enhanced the loading capacity while preserving the structural integrity of the sEVs. Additionally, lysosomal escape is facilitated by functionalizing sEVs with pH-responsive peptides, fully harnessing the inherent homing effect of sEVs for targeted and precise delivery. These sEVs achieved a 1.74-fold increase in cytosolic cargo delivery compared to unmodified sEVs, resulting in substantial gene silencing of around 73%. Our approach has significant potential to advance sEV-based gene delivery in order to accelerate clinical progress.
Keywords: GALA; gene delivery; graphene quantum dots; lipid nanoparticles; lysosomal escape.
Figures


References
-
- Johnston J; Stone T; Wang Y Biomaterial-enabled 3D cell culture technologies for extracellular vesicle manufacturing. Biomater. Sci 2023, 11 (12), 4055. - PubMed
-
- Li Z; Ho W; Bai X; Li F; Chen YJ; Zhang XQ; Xu X Nanoparticle depots for controlled and sustained gene delivery. J. Controlled Release 2020, 322, 622–631. - PubMed
-
- Kauffman KJ; Dorkin JR; Yang JH; Heartlein MW; DeRosa F; Mir FF; Fenton OS; Anderson DG Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations for mRNA Delivery in Vivo with Fractional Factorial and Definitive Screening Designs. Nano Lett. 2015, 15 (11), 7300. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
