Salmonella enterica Serovar Abony Outbreak Caused by Clone of Reference Strain WDCM 00029, Chile, 2024
- PMID: 39714466
- PMCID: PMC11682822
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3101.241012
Salmonella enterica Serovar Abony Outbreak Caused by Clone of Reference Strain WDCM 00029, Chile, 2024
Abstract
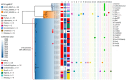
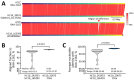
A Salmonella enterica serovar Abony outbreak occurred during January-April 2024 in Chile. Genomic evidence indicated that the outbreak strain was a clone of reference strain WDCM 00029, which is routinely used in microbiological quality control tests. When rare or unreported serovars cause human infections, clinicians and health authorities should request strain characterization.
Keywords: Chile; Salmonella enterica; WDCM 00029; bacteria; enteric infections; food safety; outbreak; serovar Abony.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome of a European fresh-vegetable food safety outbreak strain of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar weltevreden.J Bacteriol. 2011 Apr;193(8):2066. doi: 10.1128/JB.00123-11. Epub 2011 Feb 4. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21296964 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of WGS based approaches for investigating a food-borne outbreak caused by Salmonella enterica serovar Derby in Germany.Food Microbiol. 2018 May;71:46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2017.08.017. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Food Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29366468
-
Recurrent outbreaks caused by the same Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis clone in a German rehabilitation oncology clinic from 2002 to 2009.J Hosp Infect. 2018 Dec;100(4):e233-e238. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2018.03.035. Epub 2018 Mar 31. J Hosp Infect. 2018. PMID: 29614246
-
Genomic diversity of Salmonella enterica isolated from papaya samples collected during multiple outbreaks in 2017.Microbiology (Reading). 2020 May;166(5):453-459. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000895. Microbiology (Reading). 2020. PMID: 32100709
-
Emergence of a Novel Salmonella enterica Serotype Reading Clonal Group Is Linked to Its Expansion in Commercial Turkey Production, Resulting in Unanticipated Human Illness in North America.mSphere. 2020 Apr 15;5(2):e00056-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00056-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32295868 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development of a robust FT-IR typing system for Salmonella enterica, enhancing performance through hierarchical classification.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jul;13(7):e0015925. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00159-25. Epub 2025 May 27. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40422737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ikuta KS, Swetschinski LR, Robles Aguilar G, Sharara F, Mestrovic T, Gray AP, et al.; GBD 2019 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global mortality associated with 33 bacterial pathogens in 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2022;400:2221–48. 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02185-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Data Centre for Microorganisms. Salmonella enterica serovar Abony WDCM 00029 [cited 2024 Jun 7]. https://refs.wdcm.org/browse/getinfo?sid=WDCM_00029
-
- American Type Culture Collection. Salmonella enterica serovar Abony ATCC BAA-2162 [cited 2024 Jun 7]. https://www.atcc.org/products/baa-2162
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

