Impact of Hedgehog modulators on signaling pathways in primary murine and human hepatocytes in vitro: insights into liver metabolism
- PMID: 39714734
- PMCID: PMC11821798
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-024-03931-y
Impact of Hedgehog modulators on signaling pathways in primary murine and human hepatocytes in vitro: insights into liver metabolism
Abstract
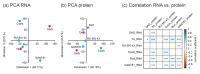
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway is essential for maintaining homeostasis during embryogenesis and in adult tissues. In the liver, dysregulation of this pathway often leads to liver cancer development. Recent studies also suggest that disturbances in the Hh pathway can affect liver metabolism in healthy livers through interactions with other signaling pathways, such as the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. As a result, the Hh pathway has emerged as a promising target for therapeutic intervention. However, little is known about the effects of Hh modulators on healthy hepatocytes. In our study, we investigated the effects of the Hh agonists SAG (300 nM) and triamcinolone acetonide (40 µM), as well as the antagonists RU-SKI 43 (100 nM), cyclopamine (5 µM), budesonide (25 µM), GANT61 (0.5 µM), and vismodegib (1 µM) on healthy mouse and human primary hepatocytes in vitro. We employed toxicological, transcriptomic, proteomic, and functional assays, including proliferation and Seahorse assays. Our results show that these compounds significantly impact metabolic pathways such as lipid and glucose metabolism at both transcriptional and protein levels. Mechanistically, our data suggest the involvement of both canonical and non-canonical Hedgehog pathways, a phenomenon not previously described in hepatocytes. These findings highlight the diverse effects of these compounds on signaling and key metabolic functions in the liver, which emphasizes the need to investigate the hepatic Hh cascade and its metabolic control in depth. As the compounds regulate different aspects of metabolism, they need to be carefully studied in appropriate model systems for specific therapeutic use.
Keywords: Activator; Hedgehog signaling; Hepatocytes; Human; Inhibitor; Modulator; Murine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Ethical approval: The mice used in this study were maintained according to European (Directive 2010/63/EU) and German guidelines for the care and safe use of experimental animals. The animal experiments were approved by the Landesdirektion Sachsen (permission numbers: T03/18; T09/22). For human hepatocytes: All patients gave their informed consent according to the ethical guidelines of the Medical Faculty of Leipzig University (Ethical vote: registration number 322/17-ek, date 2020/06/10 ratified on 2021/11/30 and registration number 422/21-ek, date 2021/11/10).
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

