Early Improvements With Atogepant for the Preventive Treatment of Migraine: Results From 3 Randomized Phase 3 Trials
- PMID: 39715475
- PMCID: PMC11668519
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000210212
Early Improvements With Atogepant for the Preventive Treatment of Migraine: Results From 3 Randomized Phase 3 Trials
Abstract
Background and objectives: Three phase 3 trials demonstrated the efficacy and safety of atogepant in episodic migraine (EM) and chronic migraine (CM) across 12-week treatment periods. This analysis evaluates improvements in efficacy and functional outcomes in the first 4 weeks of treatment with the oral calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist, atogepant, for the preventive treatment of migraine.
Methods: ADVANCE, ELEVATE, and PROGRESS were phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 12-week trials. ADVANCE and ELEVATE included participants aged 18-80 years with >1 year history of EM and 4-14 monthly migraine days (MMDs). ELEVATE required previous treatment failures to 2-4 classes of oral preventives. PROGRESS included participants aged 18-80 years with >1 year history of CM, ≥15 monthly headache days, and ≥8 MMDs. This analysis reports the atogepant 60 mg once daily (QD) and placebo treatment arms. Outcomes included efficacy endpoints (reporting a migraine day on day 1, change from baseline in weekly migraine days [WMDs] at weeks 1-4, and in MMDs in the first 4 weeks) and functional endpoints evaluated by the Activity Impairment in Migraine-Diary (AIM-D) at weeks 1-4 and the European Quality-of-Life 5-Dimension 5-Level (EQ-5D-5L) at weeks 1-2 and 4.
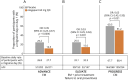
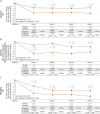
Results: The modified intent-to-treat population included the ADVANCE (atogepant, n = 222; placebo, n = 214), ELEVATE (atogepant, n = 151; placebo, n = 154), and PROGRESS (atogepant, n = 256; placebo, n = 246) studies. Atogepant-treated participants had greater reductions in the proportion of participants with a migraine day on day 1. The odds ratio compared with placebo was 0.39 (95% CI 0.23-0.67; p = 0.0006) in ADVANCE, 0.53 (95% CI 0.29-0.94, p = 0.031) in ELEVATE, and 0.63 (95% CI 0.43-0.93, p = 0.021) in PROGRESS. Atogepant treatment reduced WMDs at weeks 1-4 and MMDs in the first 4 weeks, and improved AIM-D and EQ-5D-5L at all assessed timepoints for weeks 1-4 compared with placebo.
Discussions: Atogepant 60 mg QD demonstrated superiority to placebo in efficacy and functional measures in the first 4 weeks of treatment across 3 preventive studies, 2 in EM and 1 in CM.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03777059; NCT04740827; NCT03855137. Submitted: 12/13/2018; 02/02/2021; 02/25/2019. First patient enrolled: 12/14/2018; 03/05/2021; 03/11/2019 clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03777059. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04740827 clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03855137.
Classification of evidence: This study provides Class II evidence that atogepant 60 mg QD reduces migraine frequency and improves functional outcomes within 4 weeks of initiation in patients with EM and patients with CM.
Conflict of interest statement
R.B. Lipton has received research support from the NIH, the FDA, and the National Headache Foundation; serves as a consultant for, advisory board member of, or has received honoraria or research support from AbbVie/Allergan, Amgen, Biohaven, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories (Promius), electroCore, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Lundbeck, Merck, Novartis, Teva, Vector, and Vedanta Research; receives royalties from Wolff's Headache, 8th edition (Oxford University Press, 2009), and Informa; and holds stock/options in Axon, Biohaven, CoolTech, and Manistee. C. Tassorelli has participated in advisory boards for AbbVie, Dompé, Eli Lilly, Ipsen, Lundbeck, Medscape, Pfizer, and Teva; has lectured at symposia sponsored by AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Lundbeck, Pfizer, and Teva; is principal investigator or collaborator in clinical trials sponsored by AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Ipsen, Lundbeck, Pfizer, and Teva; and has received research grants from the European Commission, the Italian Ministry of Health, the Italian Ministry of University, the Migraine Research Foundation, and the Italian Multiple Sclerosis Foundation. U. Reuter has served on advisory boards for Amgen, Allergan, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Teva; has received institutional honoraria for lectures from Amgen, Allergan, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, electroCore, Medscape, StreaMedUp, Springer, and Teva; received institutional honoraria for consulting services from Lundbeck, Pfizer, and AbbVie; received research funding from Novartis (CHERUB01) and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research; and is an associate editor of the
Figures



References
-
- Steiner TJ, Stovner LJ, Jensen R, Uluduz D, Katsarava Z, Lifting The Burden the Global Campaign against Headache. Migraine remains second among the world's causes of disability, and first among young women: findings from GBD2019. J Headache Pain. 2020;21(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s10194-020-01208-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
