Long-Term Clinical and Biological Prognostic Factors of Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis in Children
- PMID: 39715492
- PMCID: PMC12231184
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200346
Long-Term Clinical and Biological Prognostic Factors of Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis in Children
Abstract
Background and objectives: Anti-NMDAR encephalitis (NMDARE) is a severe neurologic condition, and recently, the NMDAR Encephalitis One-Year Functional Status (NEOS) score has emerged as a 1-year prognostic tool. This study aimed to evaluate NEOS score and biomarker (neurofilament light chains [NfL], total-Tau protein, glial fibrillary acidic protein, and serum cytokines) correlation with modified Rankin Scale (mRS), cognitive impairment, and clinical recovery in pediatric NMDARE over 2 years.
Methods: In this French multicenter observational study, 104 pediatric patients with NMDARE were followed for a minimum of 2 years. Clinical data and serum/plasma samples were collected. Biomarker levels, measured using electroluminescence mesoscale discovery (MSD) S-PLEX, were compared between patients and controls and assessed for correlations with disease activity, mRS, cognitive/language impairment, and recovery status at 2 years.
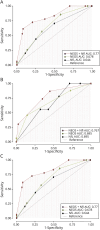
Results: At a median follow-up of 39.5 months, 68 percent of patients had unfavorable recovery and 54% had significant cognitive impairment. Both outcomes were strongly associated with younger age at diagnosis (OR 6.10 [1.91-27.3] p < 0.01 and 5.69 [1.46-27.7] p = 0.02, respectively). A higher NEOS score was significantly correlated with increased cognitive impairment (OR 2.53 [1.52-4.21], p < 0.001), higher mRS scores (OR 2.12 [1.34-3.57], p < 0.01), and unfavorable recovery at 2 years (OR 2.00 [1.30-3.06], p = 0.015). Elevated NfL levels were significantly associated with unfavorable recovery (OR 3.62 [1.29-10.9] p = 0.012) and severe cognitive impairment (OR 3.77 [1.38-10.9] p = 0.012) at 2 years. The combined area under the curve (AUC) for NfL and NEOS was significantly higher than the AUCs of NEOS and NfL alone (p = 0.01).
Discussion: The NEOS score strongly predicts long-term outcomes in NMDARE, with its predictive value extending beyond the first-year mR prediction. NfL levels at disease onset seem to improve accuracy in predicting poor outcomes, providing valuable information for treatment decisions and future clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no relevant disclosures. Go to
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
