Identification of STAT3 phosphorylation inhibitors using generative deep learning, virtual screening, molecular dynamics simulations, and biological evaluation for non-small cell lung cancer therapy
- PMID: 39715975
- PMCID: PMC12245994
- DOI: 10.1007/s11030-024-11067-5
Identification of STAT3 phosphorylation inhibitors using generative deep learning, virtual screening, molecular dynamics simulations, and biological evaluation for non-small cell lung cancer therapy
Abstract
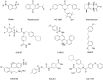
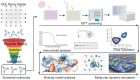
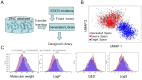
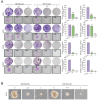
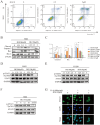
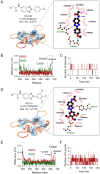
The development of phosphorylation-suppressing inhibitors targeting Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) represents a promising therapeutic strategy for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In this study, a generative model was developed using transfer learning and virtual screening, leveraging a comprehensive dataset of STAT3 inhibitors to explore the chemical space for novel candidates. This approach yielded a chemically diverse library of compounds, which were prioritized through molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Among the identified candidates, the HG110 molecule demonstrated potent suppression of STAT3 phosphorylation at Tyr705 and inhibited its nuclear translocation in IL6-stimulated H441 cells. Rigorous MD simulations further confirmed the stability and interaction profiles of top candidates within the STAT3 binding site. Notably, HG106 and HG110 exhibited superior binding affinities and stable conformations, with favorable interactions involving key residues in the STAT3 binding pocket, outperforming known inhibitors. These findings underscore the potential of generative deep learning to expedite the discovery of selective STAT3 inhibitors, providing a compelling pathway for advancing NSCLC therapies.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Drug design; Molecular dynamics; NSCLC; Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

