Comparison of remimazolam and sevoflurane for general anesthesia during transcatheter aortic valve implantation: a randomized trial
- PMID: 39715979
- PMCID: PMC11961503
- DOI: 10.1007/s12630-024-02900-4
Comparison of remimazolam and sevoflurane for general anesthesia during transcatheter aortic valve implantation: a randomized trial
Abstract
Purpose: Safe perioperative management of patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) is crucial. Remimazolam is a newly developed short-acting benzodiazepine. We hypothesized that combining remimazolam and flumazenil would reduce emergence time compared with sevoflurane in patients undergoing general anesthesia for TAVI.
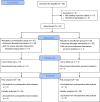
Methods: We conducted a prospective, randomized, parallel-design, open-label, single-centre clinical trial between June 2022 and August 2023 at Kagoshima University Hospital. We allocated patients randomly to either the remimazolam/flumazenil group or the sevoflurane group. Patients in the remimazolam group received iv remimazolam whereas patients in the sevoflurane group received sevoflurane for general anesthesia maintenance. Patients in both groups received a remifentanil infusion throughout the TAVI procedure (0.2 μg·kg-1·min-1 iv). Remimazolam and sevoflurane were adjusted to maintain a Bispectral Index™ (Covidien/Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA) of 40-60. In the remimazolam group, flumazenil (0.2 mg iv) was administered immediately after remimazolam discontinuation. The primary outcome was time to extubation. Secondary outcomes included intraoperative variables (hemodynamic variables and vasopressor dose), rate of intra- and postoperative complications, and recovery of muscle strength.
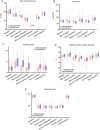
Results: Overall, 60 patients were enrolled, and data from 56 were included. The median [interquartile range] time to extubation was significantly shorter in the remimazolam group than in the sevoflurane group (6.5 [5.1-8.1] min vs 14.2 [10.9-15.9] min; difference in medians, -6.9 min; 95% confidence interval, -8.7 to -5.0; P < 0.001). Statistically significant differences were observed in the perfusion index (P = 0.03) and regional cerebral oxygen saturation (P = 0.03) between the groups. No significant differences between the two groups were seen in other secondary outcomes.
Conclusions: Compared with sevoflurane, a combination of remimazolam and flumazenil significantly reduced the time to extubation in patients undergoing general anesthesia for TAVI. Therefore, remimazolam may be a suitable choice for general anesthesia in patients undergoing TAVI.
Study registration: UMIN.ac.jp ( UMIN000047892 ); first posted 30 May 2022.
RéSUMé: OBJECTIF: Une prise en charge périopératoire sécuritaire de la patientèle bénéficiant d’une implantation valvulaire aortique via cathéter (TAVI) est cruciale. Le rémimazolam est une benzodiazépine à courte durée d’action nouvellement développée. Nous avons émis l’hypothèse que l’association du rémimazolam et du flumazénil réduirait le temps d’émergence par rapport au sévoflurane chez les personnes bénéficiant d’une anesthésie générale pour une TAVI. MéTHODE: Nous avons réalisé une étude clinique prospective, randomisée, en parallèle, ouverte et monocentrique entre juin 2022 et août 2023 à l’hôpital universitaire de Kagoshima. Nous avons aléatoirement assigné les patient·es au groupe rémimazolam/flumazénil ou au groupe sévoflurane. Les patient·es du groupe rémimazolam ont reçu du rémimazolam iv tandis que les patient·es du groupe sévoflurane ont reçu du sévoflurane pour le maintien de l’anesthésie générale. Les deux groupes ont reçu une perfusion de rémifentanil tout au long de la procédure TAVI (0,2 μg·kg−1·min−1 iv). Le rémimazolam et le sévoflurane ont été ajustés pour maintenir un indice bispectral (Covidien/Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, États-Unis) de 40 à 60. Dans le groupe rémimazolam, le flumazénil (0,2 mg iv) a été administré immédiatement après l’arrêt du rémimazolam. Le critère d’évaluation principal était le délai d’extubation. Les critères d’évaluation secondaires comprenaient les variables peropératoires (variables hémodynamiques et dose de vasopresseurs), le taux de complications peropératoires et postopératoires, et la récupération de la force musculaire. RéSULTATS: Au total, 60 patient·es ont été recruté·es et les données de 56 ont été incluses. Le délai médian [écart interquartile] jusqu’à l’extubation était significativement plus court dans le groupe rémimazolam que dans le groupe sévoflurane (6,5 [5,1–8,1] min vs 14,2 [10,9 à 15,9] min; différence entre les médianes, −6,9 min; intervalle de confiance à 95 %, −8,7 à −5,0; P < 0,001). Des différences statistiquement significatives ont été observées dans l’indice de perfusion (P = 0,03) et la saturation cérébrale régionale en oxygène (P = 0,03) entre les groupes. Aucune différence intergroupe significative n’a été observée dans les autres critères d’évaluation secondaires. CONCLUSION: Par rapport au sévoflurane, une combinaison de rémimazolam et de flumazénil a considérablement réduit le temps d’extubation chez les patient·es bénéficiant d’une anesthésie générale pour une TAVI. Par conséquent, le rémimazolam peut être un choix approprié pour l’anesthésie générale chez les patient·es bénéficiant d’une TAVI. ENREGISTREMENT DE L’éTUDE: UMIN.ac.jp ( UMIN000047892 ); première mise en ligne le 30 mai 2022.
Keywords: aortic stenosis; general anesthesia; remimazolam; sevoflurane; transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

