Association between migraine and mitochondria: A Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 39716036
- PMCID: PMC11672378
- DOI: 10.1177/17448069241298849
Association between migraine and mitochondria: A Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Background and objective: Mitochondria are important organelles functioning in metabolic processes, inflammatory response and neurological disorders. Migraines are chronic and paroxysmal neurological disorders characterized by recurrent episodes of severe headache and other neurological symptoms. We explored whether mitochondria may be genetically and/or causally associated with migraine.
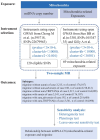
Methods: Summary-level statistics of mitochondrial DNA copy number (mtDNA-CN), 69 mitochondria related exposures and migraine with aura, migraine without aura, migraine with aura and triptan purchases, migraine with aura, drug-induced, migraine without aura and triptan purchases and migraine without aura, drug-induced, were collected from genome-wide association studies (GWAS). The analysis employed two-sample Mendelian randomization, utilizing various methods including MR-Egger, inverse-variance weighted (IVW), MR-PRESSO (MR-pleiotropy residual sum and outlier), maximum likelihood, and weighted median.
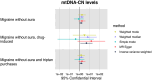
Results: We observed a potential association with decreased levels of mtDNA-CN with the risk of migraine without aura (Odds ratio (OR) 1.517, 95% Confidence interval (CI) 1.072-2.147, p = 0.019). Besides, for every 1 unit in NAD-dependent protein deacylase sirtuin-5 (SIRT5), relative risk of migraine without aura increased by 16.4%. For every 1 unit increase in Phenylalanine-transfer RNA (tRNA) ligase, relative risk of migraine without aura increased by 13.5%. For every 1 unit increase in Apoptosis-inducing factor 1, relative risk of migraine without aura increased by 27.4%.
Conclusion: This study indicates fresh evidence of association between mtDNA-CN, mitochondrial related exposures and migraine especially migraine without aura. The findings may shed light on developing interventions targeting on the causal pathway from mitochondria to migraine.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; Sirtuin-5; migraine; mitochondria; mitochondrial DNA copy number; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Dodick DW. A phase-by-phase review of migraine pathophysiology. Headache 2018; 58(Suppl. 1): 4–16. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari MD, Goadsby PJ, Roon KI, Lipton RB. Triptans (serotonin, 5-HT1B/1D agonists) in migraine: detailed results and methods of a meta-analysis of 53 trials. Cephalalgia 2002; 22: 633–658. - PubMed
-
- Brambilla R. Neuroinflammation, the thread connecting neurological disease: cluster: “neuroinflammatory mechanisms in neurodegenerative disorders”. Acta Neuropathol 2019; 137: 689–691. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

