A methodological research for development and psychometric properties of a new Measure to Assess Health Literate Organization (MAHLO-76) in hospital settings
- PMID: 39716163
- PMCID: PMC11667908
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-024-12130-5
A methodological research for development and psychometric properties of a new Measure to Assess Health Literate Organization (MAHLO-76) in hospital settings
Abstract
Background: Toward delivering appropriately safe, high quality and effective health care, healthcare organization should be health literate. This paper presents the development and psychometrics of an instrument for assessing the attributes of a health literate hospital which is called MAHLO-76 (Measure to Assess Health Literate Organization) here by authors.
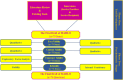
Methods: The current study is methodological research which is involved two phases of tool development and psychometric evaluation. MAHLO primary item pool was prepared using the data extracted from the semi-structured, in-depth interviews and literature review. The face and content validity were evaluated applying qualitative and quantitative approaches. Exploratory factor analysis with varimax rotation after Bartlett sphericity and KMO tests was used to evaluate the construct validity. Confirmatory factor analysis was conducted to evaluate the structural factors, applying the most common goodness-of-fit indices. In order to determine internal consistency and test-retest stability, Cronbach's alpha and intra-class correlation coefficient were calculated respectively.
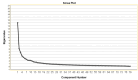
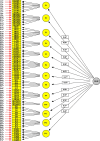
Results: The initial tool after checking for duplicates and excluding was contained 79 items. In terms of face validity, 3 items were modified using qualitative method and none of the items had an impact score of less than 1.5. In the qualitative content validity assessment, 16 items were revised and none of the items had CVR score less than 0.59 and CVI score less than 0.79. The results of the EFA obtained from the KMO showed the adequacy of the sample size (KMO value = 0.884) and the Bartlett's sphericity test showed a significant correlation between the items (χ2 = 38124.040, df = 3081, P < 0.0001). The exploratory factor analysis indicated that 14 initially extracted factors explained 63.716% of the total variance. In Confirmatory factor analysis, the chi-square was 205.016 and other model fit indices including NFI:0.812, NNFI:0.875, CFI:0.919, IFI:0.921, MFI:0.857, GFI:0.930, AGFI:0.918, RMR:0.051, RMSEA:0.06 were calculated. In reliability assessment, Cronbach's alpha was 0.94 and the value of ICC was 0.98.
Conclusion: Measure to Assess Health Literate Organization (MAHLO-76) is a valid and reliable instrument that can be used as assessment as well as self-assessment tool in hospital settings. Its application could disclosure those organizational health literacy aspects in clinical environments that need necessary interventions.
Keywords: Health literacy; Health literate organization; Hospital; Psychometric; Tool development.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The researchers observed all the ethical codes including informed consent, confidentiality, plagiarism, double publication, date manipulation, and fake data generation. This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and received approval ethical research code from ethics Committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Approval ID: IR. SBMU. PHNS. REC.1400.054: Approval Date: 2021–09–14). It should be noted that, informed consent was obtained from all participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Nutbeam D. Health literacy as a public health goal: a challenge for contemporary health education and communication strategies into the 21st century. Health Promot Int. 2000;15(3):259–67. - DOI
-
- Rudd RE, Anderson JE, Oppenheimer S, Nath C. Health literacy: an update of medical and public health literature. In: Review of Adult Learning and Literacy, Volume 7. New York: Routledge; 2023. p. 175–204.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

