Population pharmacokinetics modelling for clinical dose adjustment of carboplatin in dogs
- PMID: 39716213
- PMCID: PMC11664934
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-024-04404-1
Population pharmacokinetics modelling for clinical dose adjustment of carboplatin in dogs
Abstract
Background: Carboplatin is a human chemotherapeutic agent which is frequently used in dogs for the management of solid tumors. In human patient, its dosage is adjusted carefully, based on the creatinine clearance computation. In dogs however, the pharmacokinetics of carboplatin is poorly known and the dose 300 mg/m2 is based mostly on empirical data. Here, we aimed at characterizing the pharmacokinetics of carboplatin and determined the influence of several covariates, including creatinine plasma concentration and neutering status, in dogs, and used this model to predict myelotoxicity.
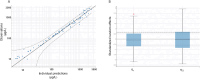
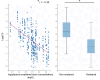
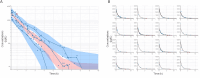
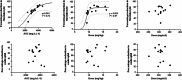
Results: Sixteen client owned dogs were included after carboplatin administration (300 mg/m2). For each animals, three to four plasma samples were collected and free plasma concentration of carboplatin was determined by HPLC/MS and analysed using Monolix® software with Non-linear mixed effect modelling. A mono-compartmental model best described the plasma concentration of carboplatin with log plasma creatinine concentration and sterilization status as covariates. After adjustment with the covariates, median population clearance was 3.62 [3.15 - 4.12] L/h/kg and volume of distribution was 3.93 [3.84 - 4.14] L/kg. The application of this model in 14 additional dogs demonstrates that individual drug exposure (model-predicted Area Under the Curve) predicted thrombocyte blood reduction (Pearson coefficient r2 = 0.73, p = 0.002) better than dose after 14 days following administration of carboplatin.
Conclusion: Based on our results, plasma creatinine concentration and the sterilization status are relevant explanatory covariates for the pharmacokinetics variability of carboplatin in client owned dogs. Dose adjustment based on these parameters could represent a promising strategy for minimizing thrombocyte toxicity.
Keywords: Carboplatin; Dogs; Modelling; Renal function; Thrombocytopenia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The protocol and the design of the study were approved by our local clinical research ethics committee (protocol #2019–03-03). All owners of the included dogs signed an informed consent before enrollment and received a detailed written description of the study. Consent for publication: All participants consents to publications of the data. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
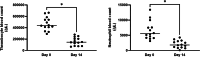
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Calvert's formula for dosage adjustment of carboplatin in Japanese patients with hormone refractory prostate cancer.Biol Pharm Bull. 2006 Jul;29(7):1441-4. doi: 10.1248/bpb.29.1441. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006. PMID: 16819185
-
Prediction of carboplatin clearance calculated by patient characteristics or 24-hour creatinine clearance: a comparison of the performance of three formulae.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1998;42(4):307-12. doi: 10.1007/s002800050822. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9744776 Clinical Trial.
-
Population pharmacokinetics of carboplatin in children.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1996 Apr;59(4):436-43. doi: 10.1016/S0009-9236(96)90113-7. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1996. PMID: 8612389 Clinical Trial.
-
[Pharmacokinetics and individual dose adjustment of carboplatin].Bull Cancer. 2000 Aug;87 Spec No:17-23. Bull Cancer. 2000. PMID: 11082718 Review. French.
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics and dose optimisation of carboplatin.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997 Sep;33(3):161-83. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199733030-00002. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997. PMID: 9314610 Review.
References
-
- Rici REG, Will SE, Luna ACL, Melo LF, Santos AC, Rodrigues RF, et al. Combination therapy of canine osteosarcoma with canine bone marrow stem cells, bone morphogenetic protein and carboplatin in an in vivo model. Vet Comp Oncol. 2018;16:478–88. - PubMed
-
- Woodruff MJ, Heading KL, Bennett P. Canine intranasal tumours treated with alternating carboplatin and doxorubin in conjunction with oral piroxicam: 29 cases. Vet Comp Oncol. 2018;17(1):42–48. - PubMed
-
- Coffee C, Roush JK, Higginbotham ML. Carboplatin-induced myelosuppression as related to body weight in dogs. Vet Comp Oncol. 2020;18:804–10. - PubMed
-
- Page RL, McEntee MC, George SL, Williams PL, Heidner GL, Novotney CA, et al. Pharmacokinetic and phase I evaluation of carboplatin in dogs. J Vet Intern Med. 1993;7:235–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

