Evolutionary variation of the monkeypox virus detected for the first time in Nantong, Jiangsu
- PMID: 39716235
- PMCID: PMC11665207
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-024-02616-3
Evolutionary variation of the monkeypox virus detected for the first time in Nantong, Jiangsu
Abstract
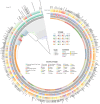
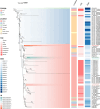
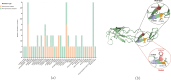
Monkeypox (MPOX) is a zoonotic disease caused by Orthopoxvirus monkeypox (MPXV), belonging to the Orthopoxvirus genus, and exhibits symptoms similar to smallpox. In 2024, the monkeypox outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo continued to develop, raising widespread global public health concerns. In September 2023, the first local monkeypox outbreak was reported in Nantong, Jiangsu Province, China. Whole-genome sequencing of samples from seven confirmed patients identified a new lineage, C.1.1, which may be related to imported cases from Japan. Evolutionary analysis of MPXV showed fewer mutations mediated by Apolipoprotein B mRNA Editing Catalytic polypeptide-like 3 (APOBEC3). Additionally, mutations in the N2L protein disrupted transcription initiation, while changes in the Cytomegalovirus-encoded immunomodulatory protein B (CrmB) led to structural instability of the protein. It is hoped that these findings will provide insights for future research on the evolutionary mechanisms of the monkeypox virus and the development of vaccines.
Keywords: APOBEC3; Monkeypox virus; Phylogenetic analysis; Single nucleotide polymorphism.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Consent for publication: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. In this study, we analyzed publicly available policy documents and government reports. Our research did not involve direct data collection or intervention involving human participants, as it is not a clinical trial. For this type of research, which does not involve direct human participation, ethics approval and consent to participate may not be applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sustained human outbreak of a new MPXV clade I lineage in eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo.Nat Med. 2024 Oct;30(10):2791-2795. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03130-3. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Nat Med. 2024. PMID: 38871006 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary trajectory and characteristics of Mpox virus in 2023 based on a large-scale genomic surveillance in Shenzhen, China.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 28;15(1):7452. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51737-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39198414 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and phenotypic insights into the first imported monkeypox virus clade Ia isolate in China, 2025.Front Public Health. 2025 Jul 9;13:1618022. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1618022. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40703185 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the biology of monkeypox virus to prevent future outbreaks.Nat Microbiol. 2024 Jun;9(6):1408-1416. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01690-1. Epub 2024 May 9. Nat Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38724757 Review.
-
Mpox: emergence following smallpox eradication, ongoing outbreaks and strategies for prevention.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2025 Jun 1;38(3):222-227. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000001100. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39878084 Review.
References
-
- Wittek R, Moss B. Tandem repeats within the inverted terminal repetition of vaccinia virus DNA. Cell. 1980;21:277–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

