Inhibition of EphA2 by syndecan-4 in wounded skin regulates clustering of fibroblasts
- PMID: 39716457
- PMCID: PMC12205308
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjae054
Inhibition of EphA2 by syndecan-4 in wounded skin regulates clustering of fibroblasts
Abstract
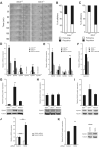
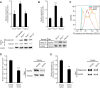
Upon injury, fibroblasts in the surrounding tissue become activated, migrating into the wound in a controlled manner. Once they arrive, they contract the wound and remodel the stroma. While certain cell surface receptors promote fibroblast migration, others cause repulsion between fibroblasts upon contact, seemingly opposing their clustering within the wound bed. Eph receptor-ephrin interactions on colliding cells trigger this repulsion, but how fibroblasts transition to clustering behaviour during healing remains unclear. Syndecan-4 modulates transmembrane receptors involved in wound healing, including receptors for the extracellular matrix and growth factors. As a result, Sdc4-/- mice experience delayed healing due to impaired fibroblast recruitment. In this study, we report that syndecan-4 also regulates fibroblast repulsion during wound healing. We discover that syndecan-4 inhibits the expression and signalling of EphA2 by activating PKCα. Changes in syndecan-4 expression, such as those observed during wound healing, alter fibroblast behaviour from repulsion to adhesion upon cell collision by modulating EphA2 levels. Moreover, we find that EphA2 expression is suppressed in wound bed fibroblasts in a syndecan-4-dependent manner, explaining how fibroblast clustering is achieved during wound healing.
Keywords: EphA2; cell migration; receptor crosstalk; syndecan-4; wound healing.
© The Author(s) (2024). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, CEMCS, CAS.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Dressings and topical agents for treating pressure ulcers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 22;6(6):CD011947. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011947.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28639707 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitor of DNA-Binding 3 Is a Novel Regulator of Limbal Epithelial Cell Migration Via the EphA2/Akt Signaling Pathway.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Jul 1;66(9):2. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.9.2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40590805 Free PMC article.
-
Active body surface warming systems for preventing complications caused by inadvertent perioperative hypothermia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 21;4(4):CD009016. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009016.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27098439 Free PMC article.
-
Negative pressure wound therapy for skin grafts and surgical wounds healing by primary intention.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Apr 18;(4):CD009261. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009261.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Oct 07;(10):CD009261. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009261.pub3. PMID: 22513974 Updated.
-
Negative pressure wound therapy for surgical wounds healing by primary closure.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 26;4(4):CD009261. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009261.pub7. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35471497 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Shed Syndecan-4 and Its Possible Roles in Osteoarthritis.Biomedicines. 2025 Apr 25;13(5):1037. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051037. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40426865 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Astin J.W., Batson J., Kadir S. et al. (2010). Competition amongst Eph receptors regulates contact inhibition of locomotion and invasiveness in prostate cancer cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 12, 1194–1204. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

