Dual-Energy Integration in Photoresponsive Micro/Nanomotors: From Strategic Design to Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 39716841
- PMCID: PMC11817945
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.202410901
Dual-Energy Integration in Photoresponsive Micro/Nanomotors: From Strategic Design to Biomedical Applications
Abstract
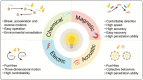
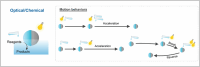
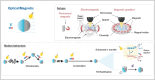
Micro/nanomotors (MNMs) are highly versatile small-scale devices capable of converting external energy inputs into active motion. Among the various energy sources, light stands out due to its abundance and ability to provide spatiotemporal control. However, the effectiveness of light-driven motion in complex environments, such as biological tissues or turbid water, is often limited by light scattering and reduced penetration. To overcome these challenges, recent innovations have integrated light-based actuation with other external stimuli-such as magnetic, acoustic, and electrical fields-broadening the functional range and control of MNMs. This review highlights the cutting-edge developments in dual-energy powered MNMs, emphasizing examples where light is paired with secondary energy sources for enhanced propulsion and task performance. Furthermore, insights are offered into the fabrication techniques, biomedical applications, and the future directions of such hybrid MNMs, while addressing the remaining challenges in this rapidly evolving field.
Keywords: biomedical applications; dual‐energy sources; multifunctional systems; photocatalytic micro/nanomotors.
© 2024 The Author(s). Small published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Photocatalytic Micro/Nanomotors: From Construction to Applications.Acc Chem Res. 2018 Sep 18;51(9):1940-1947. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00249. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Acc Chem Res. 2018. PMID: 30152999
-
Light-driven micro/nanomotors: from fundamentals to applications.Chem Soc Rev. 2017 Nov 13;46(22):6905-6926. doi: 10.1039/c7cs00516d. Chem Soc Rev. 2017. PMID: 28949354 Review.
-
[Application of self-propelled micro-/nanomotors in active targeted drug delivery].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020 Mar 30;40(3):445-452. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.03.25. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32376586 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Light-driven micro/nanomotors in biomedical applications.Nanoscale. 2023 Nov 30;15(46):18550-18570. doi: 10.1039/d3nr03760f. Nanoscale. 2023. PMID: 37962424 Review.
-
Effects of Size and Asymmetry on Catalase-Powered Silica Micro/nanomotors.Chem Asian J. 2024 Jan 15;19(2):e202300900. doi: 10.1002/asia.202300900. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Chem Asian J. 2024. PMID: 37990785
Cited by
-
Dual-source powered sea urchin-like nanomotors for intravesical photothermal therapy of bladder cancer.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 17;23(1):355. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03446-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40380217 Free PMC article.
-
Lanthanoid-doped BiVO4 microswimmers with built-in photon upconversion and light-driven motion.Chem Commun (Camb). 2025 Jul 31;61(63):11834-11837. doi: 10.1039/d5cc02091c. Chem Commun (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40625302 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling Charge Transport in Heterostructured Nanomotors for Efficient Photocatalytic Motion.Nano Lett. 2025 Jun 25;25(25):10169-10177. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5c02177. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Nano Lett. 2025. PMID: 40518840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dey K. K., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2208. - PubMed
-
- Xu L., Mou F., Gong H., Luo M., Guan J., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6905. - PubMed
-
- Šípová‐Jungová H., Andrén D., Jones S., Käll M., Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 269. - PubMed
-
- Wang Q., Dong R., Yang Q., Wang J., Xu S., Cai Y., Nanoscale Horiz. 2020, 5, 325.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

