Co-Delivery of aPD-L1 and CD73 Inhibitor Using Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles for Enhanced Melanoma Immunotherapy with Reduced Toxicity
- PMID: 39716993
- PMCID: PMC11831434
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202410545
Co-Delivery of aPD-L1 and CD73 Inhibitor Using Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles for Enhanced Melanoma Immunotherapy with Reduced Toxicity
Abstract
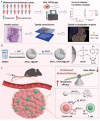
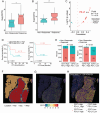
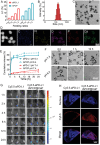
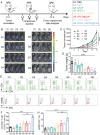
Melanoma, a malignant skin tumor, presents significant treatment challenges, particularly in unresectable and metastatic cases. While immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) targeting PD-1/PD-L1 have brought new hope, their efficacy is limited by low response rates and significant immune-mediated adverse events (irAEs). Through multi-omics data analysis, it is discovered that the spatial co-localization of CD73 and PD-L1 in melanoma correlates with improved progression-free survival (PFS), suggesting a synergistic potential of their inhibitors. Building on these insights, a novel therapeutic strategy using calcium phosphate (CaP) nanoparticles is developed for the co-delivery of aPD-L1 and APCP, a CD73 inhibitor. These nanoparticles, constructed via a biomineralization method, exhibit high drug-loading capacity and pH-responsive drug release. Compared to free aPD-L1, the CaP-delivered aPD-L1 effectively avoids systemic side effects while significantly enhancing anti-tumor efficacy, surpassing even a 20-fold dose of free aPD-L1. Furthermore, the co-delivery of aPD-L1 and APCP via CaP nanoparticles demonstrates a synergistic anti-tumor effect, with substantial immune activation and prevention of tumor recurrence through immune memory effects. These findings suggest that the co-delivery of aPD-L1 and APCP using CaP nanoparticles is a promising approach for improving melanoma immunotherapy, achieving enhanced efficacy and reduced toxicity.
Keywords: biomineralization; drug delivery; immune checkpoint inhibitors; melanoma; synergistic therapy; tumor targeting.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- a) Chen Y., Zhu J., Ding J., Zhou W., Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 108706;
- b) Long G. V., Swetter S. M., Menzies A. M., Gershenwald J. E., Scolyer R. A., Lancet 2023, 402, 485. - PubMed
-
- a) Guo J., Liu P., Wei B., Peng Y., Ding J., Zhang H., Zhang G., Su J., Liu H., Zhou W., Chen X., Nano Today 2023, 48, 101722;
- b) Brahmer J. R., Tykodi S. S., Chow L. Q., Hwu W. J., Topalian S. L., Hwu P., Drake C. G., Camacho L. H., Kauh J., Odunsi K., Pitot H. C., Hamid O., Bhatia S., Martins R., Eaton K., Chen S., Salay T. M., Alaparthy S., Grosso J. F., Korman A. J., Parker S. M., Agrawal S., Goldberg S. M., Pardoll D. M., Gupta A., Wigginton J. M., N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2455; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Hsu J. C., Liu P., Song Y., Song W., Saladin R. J., Peng Y., Hu S., Lan X., Cai W., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 7657. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Sun C., Mezzadra R., Schumacher T. N., Immunity 2018, 48, 434; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Yarchoan M., Hopkins A., Jaffee E. M., N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2500; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Li Z., Wu X., Zhao Y., Xiao Y., Zhao Y., Zhang T., Li H., Sha F., Wang Y., Deng L., Ma X., MedComm 2021, 2, 60. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022YFC2504700/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 82130090/Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 8217300/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82221002/Science Found for Creative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022RC3004/Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province
- 2023QYJC004/Central South University Research Program of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies
- 2023M733954/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 2023JJ40966/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province in China
- 2022Q13/Youth Science Foundation of Xiangya Hospital
- BX20230432/National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents
- 2023SK2095/Scientific Research Program of FuRong Laboratory
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
