Fabrication of Polydopamine-Coated High-Entropy MXene Nanosheets for Targeted Photothermal Anticancer Therapy
- PMID: 39717005
- PMCID: PMC11831489
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202410537
Fabrication of Polydopamine-Coated High-Entropy MXene Nanosheets for Targeted Photothermal Anticancer Therapy
Abstract
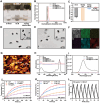
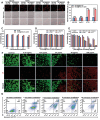
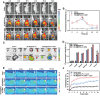
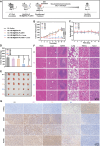
Transition metal carbides, nitrides, and carbonitrides (MXenes) have emerged as a promising class of 2D materials that can be used for various applications. Recently, a new form of high-entropy MXenes has been reported, which contains an increased number of elemental species that can increase the configurational entropy and reduce the Gibbs free energy. The unique structure and composition lead to a range of intriguing and tunable characteristics. Herein, the fabrication of high-entropy MXene TiVNbMoC3Tx (T = surface terminations) with a layer of polydopamine is reported, followed by immobilization of a phthalocyanine-based fluorophore for imaging and the peptide sequence QRHKPREGGGSC for targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) overexpressed in cancer cells. The resulting nanocomposite exhibits high biocompatibility and superior photothermal property. Upon laser irradiation at 808 nm, the light-to-heat conversion efficiency is up to 56.1%, which is significantly higher than that of conventional 2D materials. In vitro studies show that these nanosheets could be internalized selectively into EGFR-positive cancer cells and effectively eliminate these cells mainly through photothermal-induced apoptosis. Using 4T1 tumor-bearing mice as an animal model, the nanosheets could accumulate at the tumor and effectively eradicate the tumor upon laser irradiation without causing noticeable adverse effects to the mice.
Keywords: cancer therapy; epidermal growth factor receptor; high‐entropy MXenes; photothermal therapy; polydopamine.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MXene-Polydopamine-antiCEACAM1 Antibody Complex as a Strategy for Targeted Ablation of Melanoma.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Aug 21;16(33):43302-43316. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c08129. Epub 2024 Aug 7. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39111771 Free PMC article.
-
MXene-encapsulated ZIF-8@Liposomes for NIR-enhanced photothermal therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: In vitro, in vivo, and in silico study.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2025 Feb;764:110256. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2024.110256. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39638142
-
Reactive oxygen species augmented polydopamine-chlorin e6 nanosystem for enhanced chemo/photothermal/photodynamic therapy: A synergistic trimodal combination approach in vitro & in vivo.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Dec;283(Pt 1):137236. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137236. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39537079
-
Recent Advances in Photothermal Therapy at Near-Infrared-II Based on 2D MXenes.Small. 2024 Feb;20(6):e2305645. doi: 10.1002/smll.202305645. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Small. 2024. PMID: 37775938 Review.
-
Exploring the revolutionary potential of MXene nanoparticles in breast Cancer therapy: A review of applications and future prospects.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Apr 16;152:114411. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114411. Epub 2025 Mar 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40090084 Review.
References
-
- a) Hussain I., Arifeen W. U., Khan S. A., Aftab S., Javed M. S., Hussain S., Ahmad M., Chen X., Zhao J., Rosaiah P., Fawy K. F., Younis A., Sahoo S., Zhang K., Nano‐Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 215; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Shen X., Lin X., Peng Y., Zhang Y., Long F., Han Q., Wang Y., Han L., Nano‐Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 201. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Madhu S., MacKenzie J., Grewal K. S., Farooque A. A., Koleilat G. I., Selopal G. S., ChemSusChem 2024, 17, 202400421. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 14306320/Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong Special Administration Region, China
- 82272779/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023A1515030182/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2023YG022/Shenzhen University Medical-Engineering Interdisciplinary Research Fund Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
