Clinical Application of Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing (mNGS) in Patients with Early Pulmonary Infection After Liver Transplantation
- PMID: 39717063
- PMCID: PMC11665138
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S483684
Clinical Application of Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing (mNGS) in Patients with Early Pulmonary Infection After Liver Transplantation
Abstract
Purpose: To examine the clinical utility of metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) in individuals with early pulmonary infection following liver transplantation.
Patients and methods: mNGS and traditional detection results were retrospectively collected from 99 patients with pulmonary infection within one week following liver transplantation. These patients were admitted to the Department of Critical Liver Diseases at Beijing Friendship Hospital from February 2022 to February 2024, along with their general clinical data.
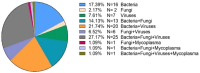
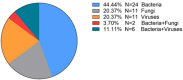
Results: mNGS exhibited a significantly higher detection rate than traditional methods (92.93% vs 54.55%, P < 0.05) and was more effective in identifying mixed infections (67.68% vs 14.81%, P < 0.05). mNGS identified 303 pathogens in 92 patients, with Enterococcus faecium, Pneumocystis jirovecii, and human herpesvirus types 5 and 7 being the most prevalent bacteria, fungi, and viruses. A total of 26 positive cases were identified through traditional culture methods (sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid), with 18 cases consistent with mNGS detection results, representing 69.23% consistency. Among the three drug-resistant bacteria that showed positivity in mNGS and traditional culture, the presence of drug-resistance genes-mecA in Staphylococcus aureus; KPC-2, KPC-9, KPC-18, KPC-26, OXA27, OXA423 in Klebsiella pneumoniae; and OXA488 and NDM6 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-reliably predicted drug-resistance phenotype. The treatment regimen for 76 of the 92 patients with positive mNGS relied on these results; 74 exhibited significant symptom improvement, yielding a 97.37% recovery rate. The overall prognosis was favorable.
Conclusion: mNGS offers rapid detection, a high positivity rate, insensitivity to antibiotics, and a superior ability to detect mixed infections in patients with early post-transplant pulmonary infections. Additionally, mNGS shows good consistency with traditional culture and can predict drug-resistant phenotypes to guide targeted antibiotic therapy for early-stage post-transplant pulmonary infection after liver transplantation. Patients whose antibiotic therapy is based on mNGS results have experienced decreased mortality rates and overall improved prognosis.
Keywords: Clinical value; Liver transplantation; Metagenomic next-generation sequencing; Pulmonary infection.
© 2024 Peng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

