Screening and molecular mechanism research on bile microRNAs associated with chemotherapy efficacy in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 39717085
- PMCID: PMC11664176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111437
Screening and molecular mechanism research on bile microRNAs associated with chemotherapy efficacy in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
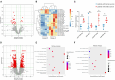
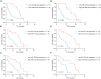
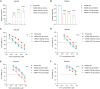
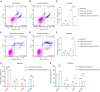
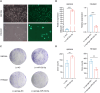
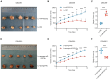
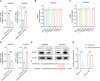
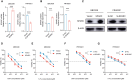
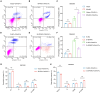
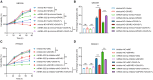
The efficacy of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) with oxaliplatin (OXA) and 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu) for treating advanced perihilar cholangiocarcinoma (pCCA) has been demonstrated, yet the survival benefits of HAIC for pCCA patients vary. Here, we aimed to screen out HAIC resistance-related bile microRNAs (miRNAs) and explore the functions of specific bile miRNAs in pCCA based on high-throughput sequencing. Levels of bile miR-532-3p, miR-1250-5p, and miR-4772-5p were related to the survival of advanced pCCA patients after HAIC. However, only overexpression of miR-532-3p promoted OXA/5-Fu resistance, and downregulation of its expression improved sensitivity to OXA/5-Fu. Mechanistic investigations revealed secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) as the direct target of miR-532-3p. Our study reveals that bile miR-532-3p, miR-1250-5p, and miR-4772-5p may serve as survival biomarkers in advanced pCCA patients after HAIC and that bile miR-532-3p promotes resistance to HAIC with OXA and 5-Fu via negatively regulating SPARC expression.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell biology; Molecular biology.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

