Trace element zinc metabolism and its relation to tumors
- PMID: 39717098
- PMCID: PMC11664221
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1457943
Trace element zinc metabolism and its relation to tumors
Abstract
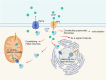
Zinc is an essential trace element in the human body, playing a crucial role in cellular metabolism.Dysregulation of zinc homeostasis can lead to abnormal cellular metabolism, contributing to diseases and closely related to tumor development. Adequate zinc intake can maintain zinc homeostasis in the body and support normal cellular metabolism. This review discusses the metabolic processes of zinc in the human body and its close relationship with tumorigenesis. It briefly describes zinc absorption, transport, storage, and release, as well as its important role in gene expression, signal transduction, oxidative stress, immune response, and apoptosis. It focuses on the abnormal cellular metabolism caused by excessive or insufficient zinc, the relationship between zinc homeostasis disruption and metabolic syndrome, and the mechanisms involved in tumor development. It analyzes how changes in the expression and activity of zinc transporters may lead to disrupted zinc homeostasis in tumor tissues. It points out that zinc deficiency is associated with various cancers, including prostate cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and breast cancer. The summary emphasizes that zinc metalloproteins could serve as potential targets for cancer therapy, and regulating the expression and activity of zinc transport proteins may offer new methods and strategies for clinical cancer treatment.
Keywords: cancer therapy; controversy; metabolic syndrome; zinc; zinc metabolism.
Copyright © 2024 Yao, Wang, Xie, Zhanghuang and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical