Neuron stress-related genes serve as new biomarkers in hypothalamic tissue following high fat diet
- PMID: 39717104
- PMCID: PMC11663644
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1443880
Neuron stress-related genes serve as new biomarkers in hypothalamic tissue following high fat diet
Abstract
Objective: Energy homeostasis is modulated by the hypothalamic is essential for obesity progression, however, the gene expression profiling remains to be fully understood.
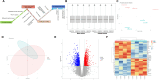
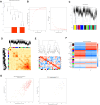
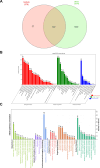
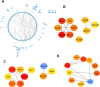
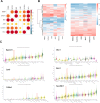
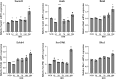
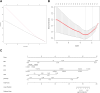
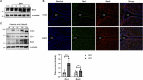
Methods: GEO datasets were downloaded from the GEO website and analyzed by the R packages to obtain the DEGs. And, the WGCNA analysis and PPI networks of co-expressed DEGs were designed using STRING to get key genes. In addition, the single-cell sequencing datasets and GTEx database were utilized to receive the neuron-stress genes from the key genes. Further, high-fat diet (HFD)-induced hypothalamic tissue of mice was used as an animal model to validate the mRNA up-regulation of neuron-stress genes. In addition, the Bmi1 gene was identified as a hub gene through the LASSO model and nomogram analysis. Western blot confirmed the high expression of Bmi1 in hypothalamic tissue of HFD mice and PA-stimulated microglia. Immunofluorescence staining showed that HFD induced the activation of microglia and the expression of Bmi1 in hypothalamic tissue.
Results: We found that six genes (Sacm1l, Junb, Bmi1, Erbb4, Dkc1, and Suv39h1) are neuron stress-related genes and increased in the HFD-induced mice obesity model, Bmi1gene was identified as a key genes that can reflect the pathophysiology of obesity.
Conclusions: Our research depicted a comprehensive activation map of cell abnormality in the obese hypothalamus and Bim1 may be a diagnostic marker in the clinic, which provides a new perspective and basis for investigating the pathogenesis of obesity.
Keywords: BMI1; WGCNA; hypothalamic inflammation; neuron stress; obesity.
Copyright © 2024 Liang, Lu, Wang, Su, Qi, Shang, Li, Zhang and Duan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identifying of immune-associated genes for assessing the obesity-associated risk to the offspring in maternal obesity: A bioinformatics and machine learning.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Mar;30(3):e14700. doi: 10.1111/cns.14700. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 38544384 Free PMC article.
-
Visceral adipose tissue imparts peripheral macrophage influx into the hypothalamus.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Jun 21;18(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02183-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34154608 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte IKKβ/NF-κB signaling is required for diet-induced obesity and hypothalamic inflammation.Mol Metab. 2017 Jan 28;6(4):366-373. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.01.010. eCollection 2017 Apr. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28377875 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the immunoproteasome in hypothalamic neurons as a novel therapeutic strategy for high-fat diet-induced obesity and metabolic dysregulation.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Aug 2;21(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03154-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 39095788 Free PMC article.
-
CX3CL1 Action on Microglia Protects from Diet-Induced Obesity by Restoring POMC Neuronal Excitability and Melanocortin System Activity Impaired by High-Fat Diet Feeding.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 7;23(12):6380. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126380. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35742824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abarca-Gómez L, Abdeen ZA, Hamid ZA, Abu-Rmeileh NM, Acosta-Cazares B, Acuin C, et al. . Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. (2017) 390:2627–42. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

