Cardiometabolic Index is associated with heart failure: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES
- PMID: 39717172
- PMCID: PMC11663657
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1507100
Cardiometabolic Index is associated with heart failure: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES
Abstract
Introduction: Heart failure is a complex syndrome characterized by impaired cardiac function. Despite improvements in treatment, the prevalence of heart failure continues to rise. The Cardiometabolic Index (CMI), a novel measure combining abdominal obesity and lipid levels, has emerged as a potential predictor of cardiac metabolic risk.
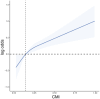
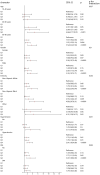
Methods: We analyzed data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) involving 22,586 participants to investigate the association between CMI and heart failure. Multivariable logistic regression models and RCS analysis were used to explore the association between heart failure and CMI after adjusting for potential confounders. Subgroup analyses were performed among populations with different demographic and clinical characteristics.
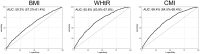
Results: Our results revealed a significant positive correlation between CMI and heart failure, with odds ratios of 2.77 and 1.87 for the highest quartile after adjusting for confounders. Subgroup analyses indicated heightened risks among older adults and those with hypertension or diabetes. ROC curve analysis demonstrated that CMI offers good diagnostic value for heart failure, surpassing traditional measures like BMI.
Discussion: Our findings suggest that CMI is a valuable tool for assessing the risk of heart failure, particularly in individuals with increased abdominal obesity or abnormal lipid profiles. This highlights the importance of addressing cardiac metabolic health in both prevention and treatment strategies for heart failure. Future research should focus on exploring causal relationships and refining predictive models that incorporate CMI to enhance early detection and intervention.
Keywords: Cardiometabolic Index; NHANES; heart failure; lipids; prevention strategies.
Copyright © 2024 Zhu, Xu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiometabolic index as a predictor of gallstone incidence in U.S. adults: insights from NHANES 2017-2020.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Jan 29;25(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03642-3. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39881275 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the nonlinear association between cardiometabolic index and hypertension in U.S. Adults: an NHANES-based study.BMC Public Health. 2025 Mar 21;25(1):1092. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22231-3. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40119367 Free PMC article.
-
Association between cardiometabolic index and myocardial Infarction: based on NHANES database.Acta Cardiol. 2025 Apr;80(2):163-172. doi: 10.1080/00015385.2025.2460404. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Acta Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 39950200
-
Relationship between Cardiometabolic index and endometriosis in a US nationally representative sample: results from NHANES 1999-2006.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 12;15:1450965. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1450965. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39600949 Free PMC article.
-
Association between cardiometabolic index and congestive heart failure among US adults: a cross-sectional study.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Sep 10;11:1433950. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1433950. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39318833 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessment of the Association Between Cardiac Metabolic Markers and Carotid Atherosclerosis, and the Role of Insulin Resistance.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 Aug 15;18:2899-2911. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S539166. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 40837609 Free PMC article.
-
Linking metabolic score for visceral fat to heart failure: insights from national health and nutrition examination survey 2003-2018.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Jul 10;24(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02654-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40640908 Free PMC article.
-
The Interplay of Cardiometabolic Syndrome Phenotypes and Cardiovascular Risk Indices in Patients Diagnosed with Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 27;26(13):6227. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136227. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650007 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources