A GD (Gamma-Delta) type of cancel culture
- PMID: 39717204
- PMCID: PMC11664092
- DOI: 10.1016/j.iotech.2024.100740
A GD (Gamma-Delta) type of cancel culture
Abstract
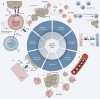
γδ T cells represent an 'unconventional' class of CD3+ lymphocytes with unique phenotypical and functional attributes that distinguishes them from their αβ T-cell receptor-expressing counterparts. Studies investigating the roles of γδ T cells in cancer have shown that these cells are indispensable for effective tumor control and their presence within the tumor may be of prognostic significance. Currently, there is significant interest in harnessing γδ T cells for cancer treatment, and research efforts have focused on the development of γδ T-cell-based strategies that are efficacious against cancer. Several therapeutic approaches using γδ T cells have been described, premised on the expansion of γδ T cells or γδ chimeric antigen receptor T therapy. The potential for broad, unbiased and 'off-the-shelf' applicability in cancer treatment, drives ongoing and future research and methodologies by which γδ T cells can be exploited for therapeutic use. In this review, we will briefly outline the characteristics of γδ T cells and describe how these work within and promote proper functioning of the cancer-immunity cycle. Additionally, we will introduce strategies that are less commonly described and may potentially be more efficacious than other types of therapy. Our discussion will expand upon presently known applications and even highlight the versatility of this immune subset as cancer therapeutics. γδ T-cell-based treatment is an emerging strategy and should be considered for cancelling cancer.
Keywords: T-cell product manufacturing/scalability; T-cell therapy for patients with solid tumors; tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL).
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
NGI sits on the scientific advisory boards of PairX Therapeutics, VerImmune and Vivo Surgical, and has received honoraria/funding from Merck, Kalbe Biotech and Agilent, all of which are outside the scope of this submitted work. WKL has declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bispecific antibodies enhance tumor-infiltrating T cell cytotoxicity against autologous HER-2-expressing high-grade ovarian tumors.J Leukoc Biol. 2020 Jun;107(6):1081-1095. doi: 10.1002/JLB.5MA1119-265R. Epub 2019 Dec 13. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. PMID: 31833593 Free PMC article.
-
γδ T Cells for Leukemia Immunotherapy: New and Expanding Trends.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 22;12:729085. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.729085. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34630403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Killing of laminin receptor-positive human lung cancers by tumor infiltrating lymphocytes bearing gammadelta(+) t-cell receptors.J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Apr 3;88(7):436-41. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.7.436. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996. PMID: 8618235
-
Universal Ready-to-Use Immunotherapeutic Approach for the Treatment of Cancer: Expanded and Activated Polyclonal γδ Memory T Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 22;10:2717. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02717. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31824502 Free PMC article.
-
Human γδ T Cell Subsets and Their Clinical Applications for Cancer Immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 18;14(12):3005. doi: 10.3390/cancers14123005. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740670 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mensurado S., Blanco-Domínguez R., Silva-Santos B. The emerging roles of γδ T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2023;20(3):178–191. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

