Comparative Evaluation of Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Effects of Escitalopram, Crocin, and their Combination in Rats
- PMID: 39717248
- PMCID: PMC11665166
- DOI: 10.4103/abr.abr_259_23
Comparative Evaluation of Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Effects of Escitalopram, Crocin, and their Combination in Rats
Abstract
Background: Chronic stress can lead to anxiety and depression. Escitalopram is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), and crocin is a natural compound derived from saffron. Both of them are used to treat these disorders in clinical and traditional medicine, respectively. This study compared the antidepressant and anxiolytic effects of escitalopram, crocin, and their combination in rats.
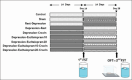
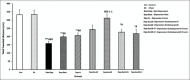
Materials and methods: Rats were divided into nine groups: control, sham, rest-depression, depression-rest, depression-crocin, depression-escitalopram10, depression-escitalopram20, depression-escitalopram10-crocin, and depression-escitalopram20-crocin. Forced swimming and open field tests (FST and OFT, respectively) were used to evaluate depression, anxiety, and locomotor activity.
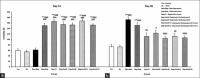
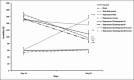
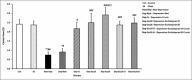
Results: In the FST, the immobility time on day 28 significantly decreased in all depressed groups that received escitalopram, crocin, and their combination compared to the rest-depression group. Whereas, conversely, the time spent at the center in the OFT was significantly higher in similar comparisons. The total distance traveled by the OFT was significantly lower in all depressed groups, except for the depression-escitalopram10 and depression-escitalopram20 groups. The total distance traveled was significantly higher in the depression-escitalopram20 compared to the rest-depression group.
Conclusion: Crocin, both doses of escitalopram and their combination, reduced depression. A high dose of escitalopram, with and without crocin, was partially more effective than a low dose of escitalopram in reversing depression. There was anxiety-like behavior observed after inducing depression with and without a recovery period. Whereas, crocin alone and both doses of escitalopram, with and without crocin, decreased anxiety-like behaviors in subjects with depression. This effect may be attributed to a modulation of brain neurotransmitter ratios.
Keywords: Crocin; depression; escitalopram; immobilization; stress.
Copyright: © 2024 Advanced Biomedical Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparing the Therapeutic Effects of Crocin, Escitalopram and Co-Administration of Escitalopram and Crocin on Learning and Memory in Rats with Stress-Induced Depression.Malays J Med Sci. 2021 Aug;28(4):50-62. doi: 10.21315/mjms2021.28.4.6. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Malays J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34512130 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanisms of action of antidepressants: new data from Escitalopram].Encephale. 2003 May-Jun;29(3 Pt 1):259-65. Encephale. 2003. PMID: 12876551 French.
-
The antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects following co-treatment with escitalopram and risperidone in rats.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;67(3):471-80. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27512008
-
[Escitalopram: a selective inhibitor and allosteric modulator of the serotonin transporter].Encephale. 2007 Dec;33(6):965-72. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2007.11.001. Epub 2007 Dec 11. Encephale. 2007. PMID: 18789789 Review. French.
-
[Efficacy and tolerability of escitalopram in anxiety disorders: a review].Encephale. 2008 Sep;34(4):400-8. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2008.04.004. Epub 2008 Aug 15. Encephale. 2008. PMID: 18922243 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Comparative assessment of antidepressant-related behaviors of citalopram, crocin, and their combination in non-acute restraint stress and acute restraint stress mice.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025 Jul 5;19:363-371. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2025.07.001. eCollection 2025 Dec. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40822001 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
