Investigating the Effect of Galbanic Acid on Lipin-1 and Lipin-2 Genes in Fatty Liver Cells with Palmitate
- PMID: 39717250
- PMCID: PMC11665169
- DOI: 10.4103/abr.abr_456_23
Investigating the Effect of Galbanic Acid on Lipin-1 and Lipin-2 Genes in Fatty Liver Cells with Palmitate
Abstract
Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is related to lipid accumulation and inflammation. Considering the role of lipin-1 and lipin-2 in fat homeostasis and inflammation, this study aimed to explore the effect of galbanic acid (Gal) and resveratrol (RSV) on alterations in the gene expression levels and protein abundance of lipin-1 and lipin-2 in HepG2 liver cells lipid-enriched with palmitate (Pal).
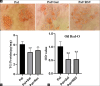
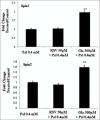
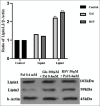
Materials and methods: HepG2 cells were subjected to different amounts of Gal and RSV for 24 hours in the presence of Pal to induce lipid accumulation. The RT-PCR method was employed to assess the expression of lipin-1 and lipin-2 genes, while protein levels were evaluated by western blot analysis. Lipid accumulation was determined qualitatively and semi-quantitatively using the oil-red staining technique.
Results: Gal treatment increased lipin-1 and lipin-2 gene expression (P < 0.05). In contrast, the groups treated with RSV did not show a substantial variance in the expression levels of the two genes (P > 0.05). In the groups treated with Gal/RSV, the intensity of lipin-2 protein bands was higher compared to the Pal group (P > 0.01); however, the intensity of lipin-1 protein bands was not significantly different (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Gal, a coumarin compound, significantly increased the expression of lipin-1 and lipin-2 in HepG2 cells treated with Pal. Consequently, this research suggests gal as a novel strategy for regulating fat homeostasis in HepG2 cells.
Keywords: Galbanic acid; lipin-1; lipin-2; non-alcoholic fatty liver; resveratrol.
Copyright: © 2024 Advanced Biomedical Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A molecular and computational study of galbanic acid as a regulator of Sirtuin1 pathway in inhibiting lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2024 Dec;130(6):877-885. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2024.2336911. Epub 2024 May 7. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38712991
-
Deletion of SIRT1 from hepatocytes in mice disrupts lipin-1 signaling and aggravates alcoholic fatty liver.Gastroenterology. 2014 Mar;146(3):801-11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.11.008. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24262277 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol protects against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by improving lipid metabolism and redox homeostasis via the PPARα pathway.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020 Mar;45(3):227-239. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2019-0057. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020. PMID: 31173696
-
Signal Transduction Mechanisms of Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Emer ging Role of Lipin-1.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2017;10(3):226-236. doi: 10.2174/1874467208666150817112109. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 26278388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian lipin phosphatidic acid phosphatases in lipid synthesis and beyond: metabolic and inflammatory disorders.J Lipid Res. 2019 Apr;60(4):728-733. doi: 10.1194/jlr.S091769. Epub 2019 Feb 25. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 30804008 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Targher G, Corey KE, Byrne CD, Roden M. The complex link between NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus-mechanisms and treatments. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18:599–612. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
