Early Detection of Diabetic Nephropathy Based on Urinary and Serum Biomarkers: An Updated Systematic Review
- PMID: 39717256
- PMCID: PMC11665175
- DOI: 10.4103/abr.abr_461_23
Early Detection of Diabetic Nephropathy Based on Urinary and Serum Biomarkers: An Updated Systematic Review
Abstract
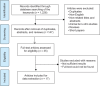
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a leading cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease worldwide, particularly among individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Early detection and intervention are crucial in slowing the progression of DN and improving patient outcomes. Traditional diagnostic methods, such as the measurement of albuminuria and serum creatinine, often fail to detect early renal damage because structural kidney damage may occur before albumin excretion. This systematic review aims to evaluate the diagnostic value of various urinary and serum biomarkers in the early detection of DN in patients with T2DM. A comprehensive literature search was conducted using databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science. We only considered studies involving human populations for inclusion in our analysis. Animal and in vitro studies were excluded from our review. Our analysis of 17 observational studies identified several key serum biomarkers, such as netrin-1, osteopontin, adiponectin, and specific cytokines (e.g., IL-6, IL-8), which show significant promise for early detection of DN. Urinary biomarkers, including neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), transferrin, N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAG), and various cytokines, have also proven to be reliable indicators. The combination of both serum and urinary biomarkers may enhance diagnostic accuracy and enable earlier intervention. Additionally, incorporating genetic and mRNA markers could provide a more comprehensive approach to early DN detection. Implementing these biomarkers in clinical practice could significantly improve outcomes for patients with DN by facilitating early diagnosis and timely management.
Keywords: Biomarkers; diabetes; diabetic nephropathy; review.
Copyright: © 2024 Advanced Biomedical Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
Application of urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase combined with serum retinol-binding protein in early detection of diabetic nephropathy.World J Diabetes. 2023 Jun 15;14(6):883-891. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i6.883. World J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37383593 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary biomarkers for early diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients.Biomark Res. 2015 Jul 4;3:16. doi: 10.1186/s40364-015-0042-3. eCollection 2015. Biomark Res. 2015. PMID: 26146561 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin for Predicting Early Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Appl Lab Med. 2019 Jul;4(1):78-94. doi: 10.1373/jalm.2018.028530. Epub 2019 Mar 1. J Appl Lab Med. 2019. PMID: 31639710
-
Comparative diagnostic utility of different urinary biomarkers during pre-albuminuric stages of non-hypertensive type 2 diabetic nephropathy.Indian J Med Res. 2022 Jul;156(1):46-55. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_455_21. Indian J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 36510897 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Markers of Tubular Injury in Early Diabetic Nephropathy.Int J Nephrol. 2016;2016:4647685. doi: 10.1155/2016/4647685. Epub 2016 May 16. Int J Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27293888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Augmented Intrarenal and Urinary Angiotensinogen in Diabetic Nephropathy: The Role of Isoflavones.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 8;26(4):1443. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041443. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Biomarkers and Advanced Diagnostics in Chronic Kidney Disease: Early Detection Through Multi-Omics and AI.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 13;15(10):1225. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15101225. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428218 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87:4–14. - PubMed
-
- Gross JL, de Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP, Canani LH, Caramori ML, Zelmanovitz T. Diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:164–76. - PubMed
-
- Zachwieja J, Soltysiak J, Fichna P, Lipkowska K, Stankiewicz W, Skowronska B, et al. Normal-range albuminuria does not exclude nephropathy in diabetic children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010;25:1445–51. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous