Evaluation of RehaCom cognitive rehabilitation on different aspects of visual attention in patients with middle cerebral artery ischemia: A nonblinded randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 39717427
- PMCID: PMC11663283
- DOI: 10.48305/arya.2024.31210
Evaluation of RehaCom cognitive rehabilitation on different aspects of visual attention in patients with middle cerebral artery ischemia: A nonblinded randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Cerebral ischemia or stroke is the second leading cause of death in the world, and most surviving patients suffer from long-term physical and cognitive disabilities, which create many social and economic problems for them and society. Visual attention impairment is a common cognitive complication among patients with cerebral ischemia, especially in the Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA). One way to improve attention in these patients is cognitive rehabilitation. RehaCom software is one of the computer-based tools to rehabilitate visual attention in these patients. The purpose of this study was to evaluate RehaCom cognitive rehabilitation on different aspects of visual attention in patients with middle cerebral artery ischemia.
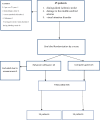
Methods: In this single-blind randomized clinical trial, 30 patients with cerebral ischemia in MCA territories were selected and randomly divided into control (n=15) and intervention (n=15) groups. Visual attention of both groups was assessed before the treatments using the Integrated Visual-Auditory test (IVA). Then the intervention group was rehabilitated for 8 sessions of 45 minutes each with RehaCom cognitive software, according to our selected modules, while the control group was only under intervention by non-targeted computer games. After applying the treatments, visual attention in the two groups was assessed using the IVA test.
Results: There were no significant differences in visual focus attention between the intervention and control groups before the intervention (29.20±30.06 and 49.53±29.69, P value >0.05). In addition, there were no significant differences in visual selective attention in both groups before the study (23.07±24.73, 39.27±27.08, P value >0.05). However, significant differences were found in visual sustained attention, visual alternating attention, and visual divided attention at baseline (P value <0.05). After the intervention, visual focus attention in the intervention group was significantly higher than in the control group (84.67±26.51, 57.20±31.44, P value <0.05). RehaCom cognitive software intervention increased visual divided attention in the intervention group (88.40±14.85 versus 72.70±25.73, P value <0.05).
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that using RehaCom cognitive software can improve focus attention and visual attention in the intervention group. Cognitive rehabilitation with RehaCom was able to improve visual attention deficits in patients with middle cerebral artery ischemia.
Keywords: Cerebral Ischemia; Cognitive Rehabilitation; Medial Cerebral Artery; RehaCom; Visual Attention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of RehaCom cognitive rehabilitation software in activities of daily living, attention and response control in chronic stroke patients.J Clin Neurosci. 2020 Jan;71:101-107. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2019.08.114. Epub 2019 Sep 5. J Clin Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31495655
-
Treatment with RehaCom computerized rehabilitation program improves response control, but not attention in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).J Clin Neurosci. 2022 Apr;98:149-153. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2022.02.008. Epub 2022 Feb 15. J Clin Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35180505
-
RehaCom rehabilitation training improves a wide-range of cognitive functions in multiple sclerosis patients.Appl Neuropsychol Adult. 2022 Mar-Apr;29(2):262-272. doi: 10.1080/23279095.2020.1747070. Epub 2020 May 5. Appl Neuropsychol Adult. 2022. PMID: 32368936 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Efficacy of Acupuncture Treatment in Combination With RehaCom Cognitive Training for Improving Cognitive Function in Stroke: A 2 × 2 Factorial Design Randomized Controlled Trial.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016 Dec 1;17(12):1114-1122. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2016.07.021. Epub 2016 Aug 31. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27592180 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of computer-based telerehabilitation software (RehaCom) compared to other treatments for patients with cognitive impairments: A systematic review.Digit Health. 2024 Nov 26;10:20552076241290957. doi: 10.1177/20552076241290957. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39600389 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Petersen A, Vangkilde S, Fabricius C, Iversen HK, Delfi TS, Starrfelt R. Visual attention in posterior stroke and relations to alexia. Neuropsychologia. 2016 Nov;:92:79–89. - PubMed
-
- Young PA, Young PH, Tolbert DL. Basic Clinical Neuroscience. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.
-
- Everts R, Pavlovic J, Kaufmann F, Uhlenberg B, Seidel U, Nedeltchev K, et al. Cognitive functioning, behavior, and quality of life after stroke in childhood. Child Neuropsychol. 2008 Jul;14(4):323–38. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources