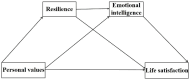
Resilience and emotional intelligence as mediators between personal values and life satisfaction among Chinese young adults
- PMID: 39717466
- PMCID: PMC11665639
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1491566
Resilience and emotional intelligence as mediators between personal values and life satisfaction among Chinese young adults
Abstract
Background: Young adults are in the period of the formation and establishment of values. Even though previous research has revealed that personal values are important factors influencing young adults' life satisfaction, it is still unknown when and under what circumstances values affect life satisfaction among young adults. Therefore, this study explored the relationship between personal values and life satisfaction among Chinese young adults, focusing on the mediating roles of resilience and emotional intelligence.
Methods: A sample of N = 635 (271 male) young adults from four universities located in Guangzhou were recruited using a cross-sectional stratified sampling method. All participants completed the Revised Portrait Value Questionnaire, Emotional Intelligence Scale, Satisfaction with Life Scale, and Brief Resilience Scale.
Results: Results revealed that: (1) self-transcendence (r = 0.29, p < 0.001), self-enhancement (r = 0.27, p < 0.001), openness to change (r = 0.22, p < 0.001), and conservation (r = 0.26, p < 0.001) were differentially positively associated with life satisfaction. Chain mediation analysis found that: there was a significant indirect effect for self-transcendence, via EI (ind = 0.070, p = 0.004, 95% CI = [0.027, 0.124]), and the sequential influence via EI and resilience suggested a moderate effect (ind = 0.024, p = 0.008, 95% CI = [0.009, 0.045]). For self-enhancement values exerted significantly negative indirect effects on LS via resilience (ind = -0.029, p = 0.034, 95% CI = [-0.060, -0.005]). Openness to change had a significant indirect impact on LS via EI (ind = 0.086, p < 0.001, 95% CI = [0.046, 0.133]), and the sequential influence via resilience and EI was significant (ind = 0.029, p = 0.001, 95% CI = [0.015, 0.050]). For conservation, the chain mediation model did not reveal any significant indirect effects via resilience or EI.
Conclusion: Our findings extend the current literature on personal values and life satisfaction, highlighting the significant effects of resilience and emotional intelligence on the link between personal values and life satisfaction. Overall, this research helps young adults strengthen their resilience and emotional intelligence to increase the impact of values on life satisfaction.
Keywords: emotional intelligence; life satisfaction; personal values; resilience; young adults.
Copyright © 2024 Lv, Tan, Shi and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring the interplay of emotional intelligence, psychological resilience, perceived stress, and life satisfaction: A cross-sectional study in the Turkish context.BMC Psychol. 2024 Jun 21;12(1):362. doi: 10.1186/s40359-024-01860-0. BMC Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38907343 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of emotional intelligence on life satisfaction among Chinese nurses: A chain mediating model.Front Psychol. 2023 Feb 17;14:1125465. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1125465. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36874842 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Intelligence, Resilience, and Self-Esteem as Predictors of Satisfaction with Life in University Students.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 9;19(24):16548. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416548. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36554428 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience as a mediator between emotional intelligence (EI) and perceived stress among young adults in Malaysia.Discov Ment Health. 2025 Mar 20;5(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s44192-025-00166-w. Discov Ment Health. 2025. PMID: 40108032 Free PMC article.
-
Academic Resilience and its Relationship With Emotional Intelligence and Stress Among University Students: A Three-Country Survey.Brain Behav. 2025 Apr;15(4):e70497. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70497. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40259642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn J. S., Reeve J. (2021). Developmental pathways of preadolescents’ intrinsic and extrinsic values: the role of basic psychological needs satisfaction. Eur. J. Personal. 35, 151–167. doi: 10.1002/per.2274 - DOI
-
- Arambewela R., Hall J. (2013). The interactional effects of the internal and external university environment, and the influence of personal values, on satisfaction among international postgraduate students. Stud. High. Educ. 38, 972–988. doi: 10.1080/03075079.2011.615916 - DOI
-
- Ardenghi S., Rampoldi G., Bani M., Strepparava M. G. (2023). Personal values as early predictors of emotional and cognitive empathy among medical students. Curr. Psychol. 42, 253–261. doi: 10.1007/s12144-021-01373-8 - DOI
-
- Asif M., Idrees M., Ghazal S., Ishaq G. (2022). Relationship of emotional intelligence and life satisfaction: mediating role of affectivity in medical students. ASEAN J. Psychiatr. 37, 135–138. doi: 10.33824/PJPR.2022.37.1.09 - DOI
-
- Athota V. S., O’Connor P. J. (2014). How approach and avoidance constructs of personality and trait emotional intelligence predict core human values. Learn. Indi. Diff. 31, 51–58. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2013.12.009 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources