Custom-Made Ce-Mn Bimetallic Nanozyme for the Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Modulating Macrophage M1/M2 Polarization
- PMID: 39717477
- PMCID: PMC11665849
- DOI: 10.34133/bmr.0118
Custom-Made Ce-Mn Bimetallic Nanozyme for the Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Modulating Macrophage M1/M2 Polarization
Abstract
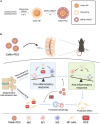
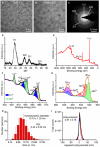
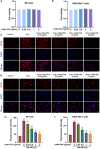
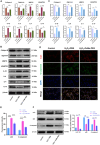
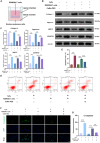
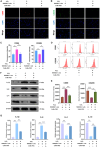
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD)-induced lower back pain (LBP) brings heavy burden worldwide. In the degenerated intervertebral disc, there is an increase in the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the infiltration of M1 macrophages, which leads to abnormal local inflammatory microenvironment and exacerbates IDD. In this study, we developed a novel injectable polyethylene glycol (PEG)-capped cerium ion-manganese ion (Ce-Mn) bimetallic nanozyme (CeMn-PEG) with strong ROS scavenging and M2-type macrophage polarizing abilities to efficiently alleviate IDD. In vitro experiments demonstrated that CeMn-PEG effectively scavenged excess ROS in both nucleus pulposus (NP) and RAW264.7 cells. In addition, we found that CeMn-PEG markedly protected NP cells from H2O2-induced overproduction of inflammatory cytokines, excessive cell apoptosis and autophagy, and imbalance between extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation. Moreover, CeMn-PEG induced macrophages to transition from the M1 phenotype to the M2 phenotype and the increased M2-type macrophages could alleviate H2O2-induced ECM degradation and cell apoptosis in NP cells. In a puncture-induced mouse IDD model, CeMn-PEG treatment could effectively ameliorate the progression of disc degeneration and mitigate puncture-induced mechanical hyperalgesia. Thus, our study demonstrated the effectiveness of CeMn-PEG as a novel treatment strategy for the treatment of IDD and a range of other inflammatory diseases.
Copyright © 2024 Jianwei Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Katz JN. Lumbar disc disorders and low-back pain: Socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(Suppl 2):21–24. - PubMed
-
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211–1259. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hudson KD, Alimi M, Grunert P, Härtl R, Bonassar LJ. Recent advances in biological therapies for disc degeneration: Tissue engineering of the annulus fibrosus, nucleus pulposus and whole intervertebral discs. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013;24(5):872–879. - PubMed
-
- Jin H, Wang Q, Wu J, Han X, Qian T, Zhang Z, Wang J, Pan X, Wu A, Wang X. Baicalein inhibits the IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates disc degeneration in vivo. Inflammation. 2019;42(3):1032–1044. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

