Imaging Lipidomics and Metallomics of Brown Rice Cultivars Used for Sake Production
- PMID: 39717497
- PMCID: PMC11664313
- DOI: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0164
Imaging Lipidomics and Metallomics of Brown Rice Cultivars Used for Sake Production
Abstract
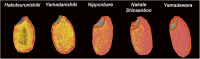
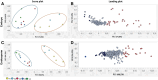
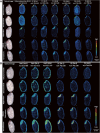
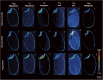
Many previous studies have reported various phospholipids and elements that affect sake production; however, it seems to be challenging to investigate individual types in each rice variety due to their high diversity, not to mention their distribution patterns. Since its introduction, mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) has gained attention in various fields as a simple compound visualization technique. The current study highlights the progress of powerful MSI in comprehensively analyzing phospholipids and minerals in brown rice for sake production. Multivariate analysis suggested phospholipids relating to each rice group based on regions of interest. Phospholipid classes connected with embryo and endosperm included fatty acylcarnitine, diacylglycerol, phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylglycerol, and phosphatidylethanolamine. Meanwhile, the studied rice groups showed the same distribution of the investigated 12 minerals. This is the first study that reports a comprehensive imaging analysis of phospholipids and elements in brown rice for several cultivars for sake production.
Keywords: general rice; lipids; mass spectrometry imaging; metals; sake rice.
Copyright © 2024 Eliza Farestiani, Yoshihiro Tamada, Koji Okuda, Eiichiro Fukusaki, and Shuichi Shimma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Shotgun lipidomics reveals the changes in phospholipids of brown rice during accelerated aging.Food Res Int. 2023 Sep;171:113073. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113073. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Food Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37330832
-
Modeling the sake brewing characteristics of rice from brown rice metabolites.J Biosci Bioeng. 2022 Aug;134(2):116-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2022.04.007. Epub 2022 May 21. J Biosci Bioeng. 2022. PMID: 35610162
-
Distribution of lysophosphatidylcholine in the endosperm of Oryza sativa rice.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2014 Jul 15;28(13):1515-20. doi: 10.1002/rcm.6927. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2014. PMID: 24861602
-
Rice used for Japanese sake making.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2019 Aug;83(8):1428-1441. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2019.1574552. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30727845 Review.
-
Mass Spectrometry Imaging for Single-Cell or Subcellular Lipidomics: A Review of Recent Advancements and Future Development.Molecules. 2023 Mar 17;28(6):2712. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062712. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985684 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- M. Okuda. Rice used for Japanese sake making. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 83: 1428–1441, 2019. - PubMed
-
- S. Okada, M. Suehiro, K. Ebana, K. Hori, A. Onogi, H. Iwata, M. Yamasaki. Genetic dissection of grain traits in Yamadanishiki, an excellent sake-brewing rice cultivar. Theor. Appl. Genet. 130: 2567–2585, 2017. - PubMed
-
- A.-K. Horigane, K. Suzuki, M. Yoshida. Moisture distribution in rice grains used for sake brewing analyzed by magnetic resonance imaging. J. Cereal Sci. 60: 193–201, 2014.
-
- K. Nagato, M. Ebata. Studies on White-Core Rice Kernel: II. On the physical properties of the kernel. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 28: 46–50, 1959 (in Japanese).
-
- M. Tamaki, S. Kurita, M. Toyomaru, T. Itani, T. Tsuchiya, I. Aramaki, M. Okuda. Difference in the physical properties of white-core and non-white-core kernels of the rice varieties for sake brewing is unrelated to starch properties. Plant Prod. Sci. 9: 78–82, 2006.

