Comprehensive analysis of IRF8-related genes and immune characteristics in lupus nephritis
- PMID: 39717551
- PMCID: PMC11663682
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1468323
Comprehensive analysis of IRF8-related genes and immune characteristics in lupus nephritis
Abstract
Background: There are currently no reliable diagnostic biomarkers or treatments for lupus nephritis (LN), a complication of systemic lupus erythematosus. Objective: We aimed to explore gene networks and potential biomarkers for LN by analyzing the GSE32591 and GSE113342 datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus database, focusing on IRF8 and IRF8-related genes.
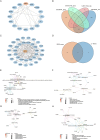
Methods: We used differential expression analysis, functional enrichment, protein-protein interaction (PPI) network construction, and the CIBERSORT algorithm for immune infiltration assessment. To validate the expression levels of the IRF8 gene in the kidneys of lupus mice models, we used quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blotting (WB). A diagnostic classifier was built using the RandomForest method to evaluate the diagnostic potential of selected key genes. To bridge our findings with potential therapeutic implications, we used the drug-gene interaction database to predict drugs targeting the identified genes.
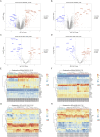
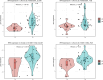
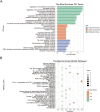
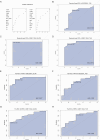
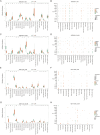
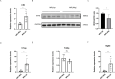
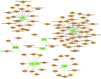
Results: Twenty co-differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified, with IRF8 exhibiting significant expression differences and potential as a biomarker. Functional enrichment analysis revealed pathways associated with immune response. Validation through qRT-PCR and WB confirmed that the IRF8 gene and its protein exhibited elevated expression levels in the kidneys of lupus mice compared to control groups. The diagnostic classifier revealed impressive accuracy in differentiating LN from control samples, achieving a notable area under the curve values across various datasets. Additionally, immune infiltration analysis indicated significant differences in the immune cell profiles between the LN and control groups.
Conclusion: IRF8 and its related genes show promise as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for LN. These findings contribute to a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in LN and may support the development of precision medicine strategies for improved patient outcomes.
Keywords: IRF8; biomarkers; drug-gene interaction; immune infiltration; lupus nephritis.
Copyright © 2024 Yu, Zheng and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

